
Some terminology for Thrust faults, duplexes, imbricate fans, and fold-thrust belts.
Thrusts are reverse faults having fault plane dips <45o, usually <30o. Thrusts are compressional structures commonly developed in layered sedimentary and foliated metamorphic rock in which mechanically strong units are interlayered with weak rock, for example dense sandstone or carbonate units and weaker shales. Thrusts tend to co-locate with other thrusts in fold-thrust systems. Some of the best-known examples occur in collisional orogens as foreland fold-thrust belts, and on the upper plate of subduction zones as accretionary wedges.
An important outcome of thrust faulting is shortening parallel to layering. For individual faults, shortening can be measured in centimetres to 100s of metres depending on size. The cumulative shortening across orogenic fold-thrust belts is often measured in 100s of kilometres.
Thrust faults are nearly always accompanied by folds, particularly in their hanging walls. Folding is a geometric and a space requirement of shortening, and a mechanism of distributing strain as the fault tip propagates. The strain generated by shortening can also be distributed as penetrative deformation such as cleavage. Thus, total shortening across a thrust system is the sum of fault displacement, folding, and cleavage.
The terminology of thrust faults has evolved, since the pioneering work by Peach and Horn, into a fairly complicated system of variations on numerous themes – fault and fold geometry, fault stacking, fault displacement, fault and fold associations. Only the most common terms are illustrated here. There are several oldish, but excellent publications that treat terminology and theory in a more encyclopedic manner: McClay 1981 (as editor of a 1981 special volume, a 1992 text, and a 2011 AAPG Memoir; in the same volume, Price 1981; blind thrusts, Thompson, 1981; Suppe, 1983 (fault bend folding); Mitra 1986, duplexes; and Dahlstrom 1969, balanced cross-sections.
Terminology (in alphabetical order)
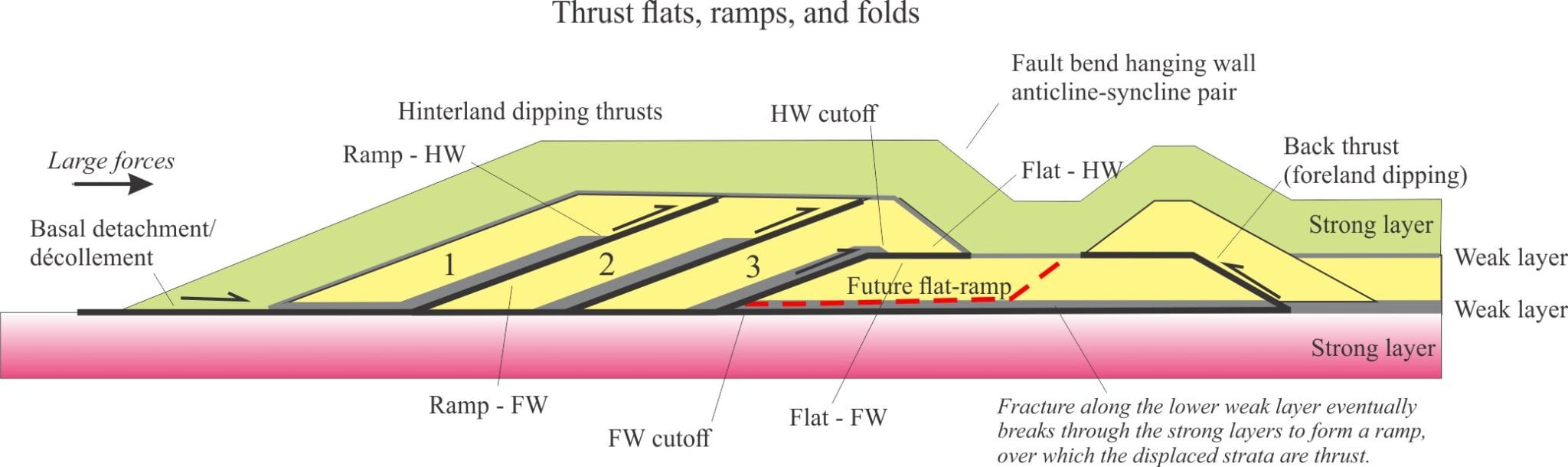
Back thrust: A thrust that has vergence opposite the dominant trend of a thrust system. In many cases back thrust vergence will be towards the hinterland, i.e. thrust plane dip is towards the foreland.
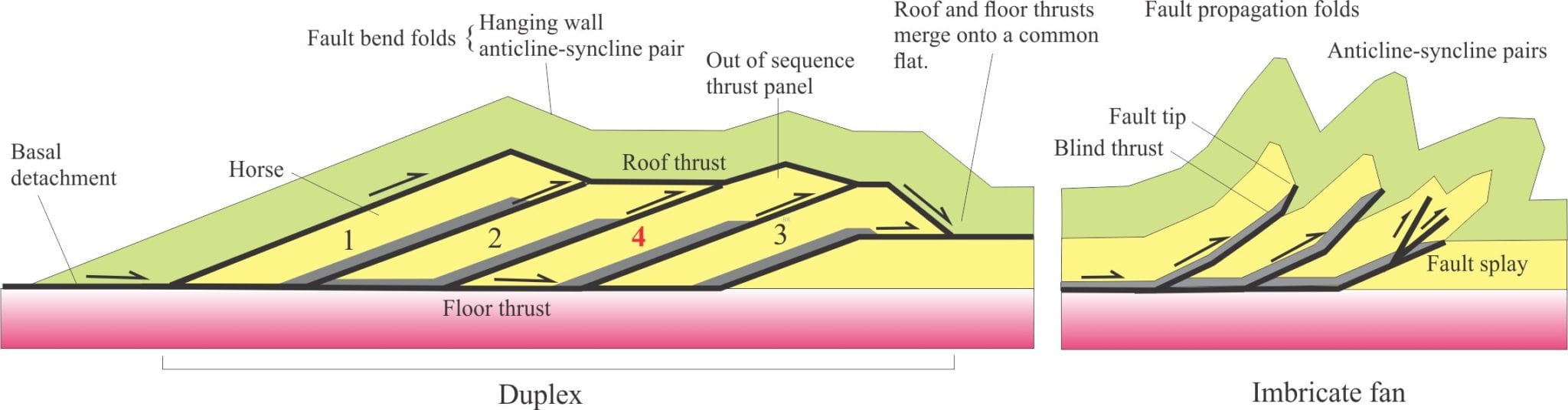
Blind thrust: A thrust that does not breach the surface at the time of its formation. Blind thrust tip points (tip lines) typically contain fault propagation fold pairs.
Branch points: Locations along a thrust where branching or fault splays are generated.
Cutoff points: The truncation of identifiable rock units or beds that can be traced across the hanging wall and footwall.
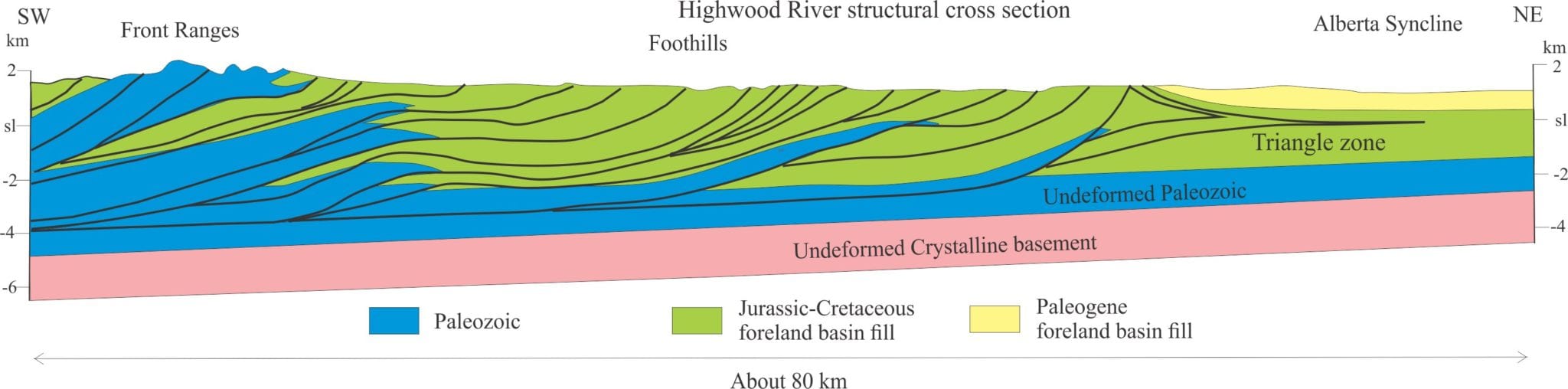
Décollement-basal detachment-sole thrust: Names given to the thrust at the base of a thrust stack, that is the common surface of detachment for all thrusts. It overlies undeformed rocks (e.g. Cratonic platform, crystalline basement). An example is shown in the fold-thrust cross section below.
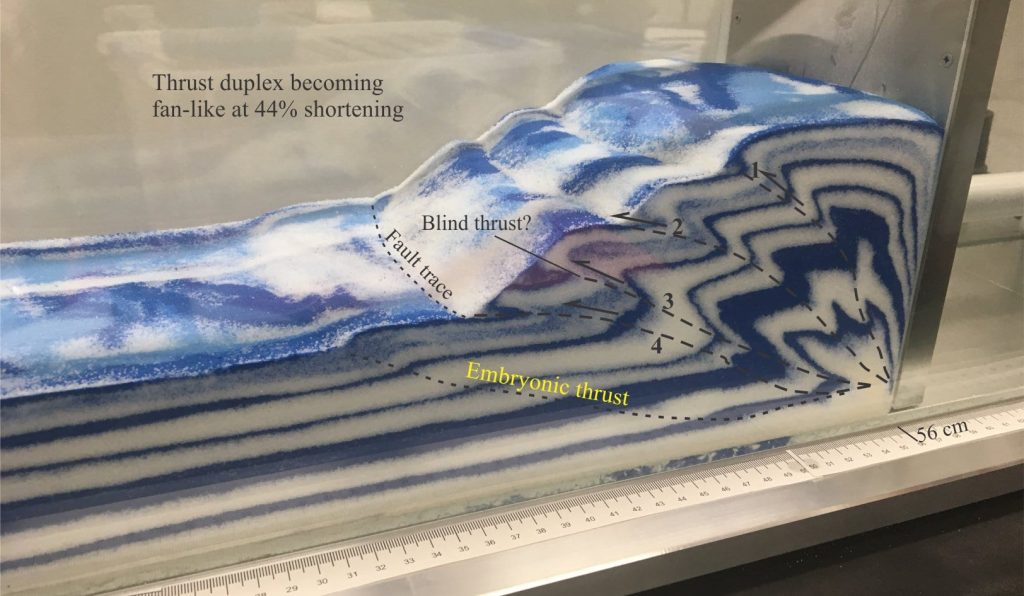
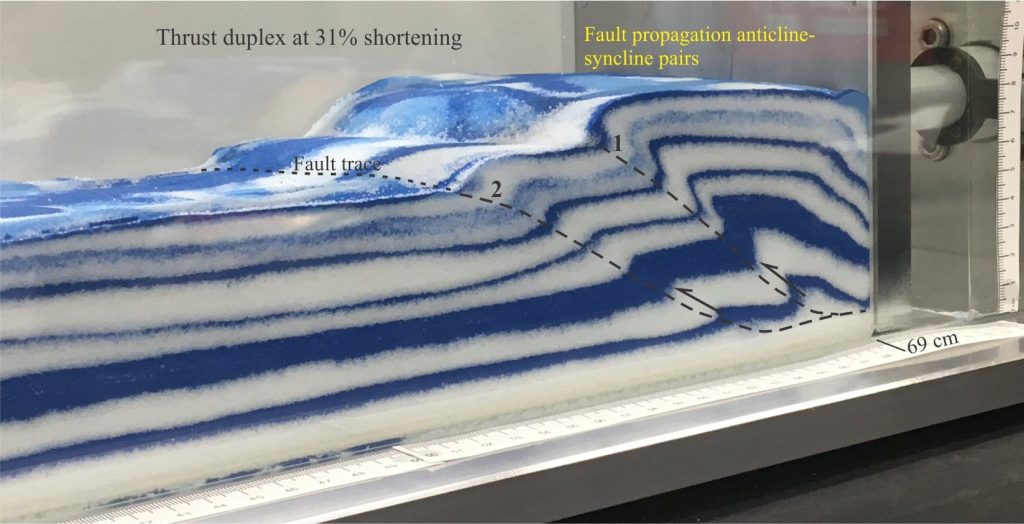
Duplex: An imbricate stack of horses bound above and below by through-going thrusts; these are the roof and floor thrusts. Duplexes represent progressive, incremental formation of ramps and bending folds (anticline-syncline pairs). Duplexes can take several geometric forms – the item illustrated below is a normal duplex; increased vertical stacking of horses produces an antiformal duplex.
Fault-bend folds: Folds that develop in the hanging wall where there is a change in the inclination of a fault plane. For thrust ramps, this includes a syncline above the flat-ramp transition, and anticline at the fault tip, thus producing a characteristic anticline-syncline pair. Compare this category of folds with those produced by fault propagation.
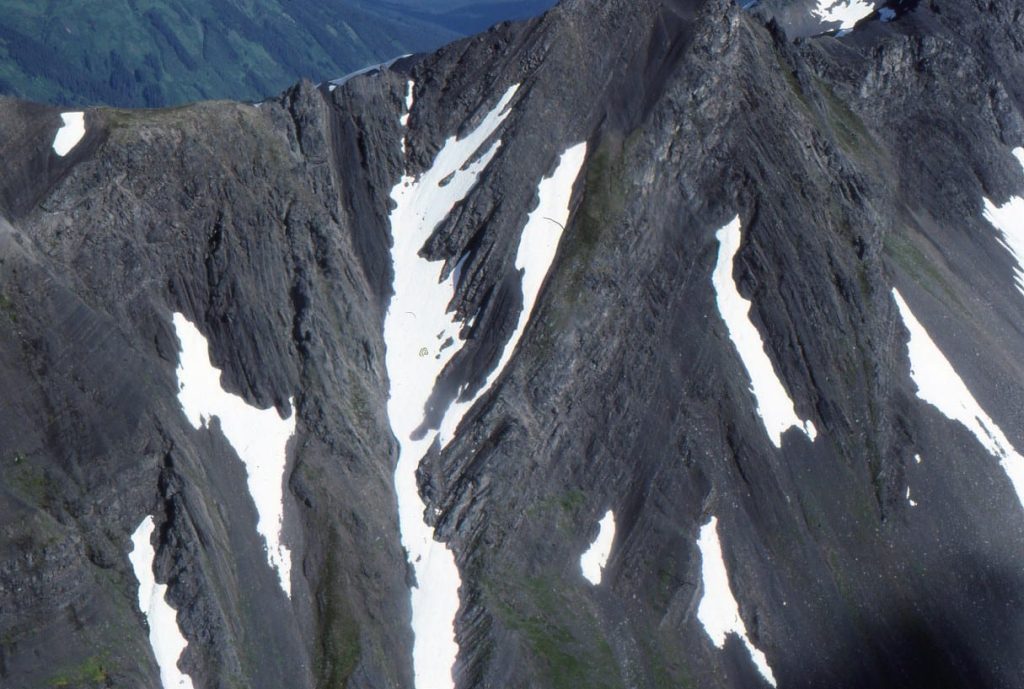
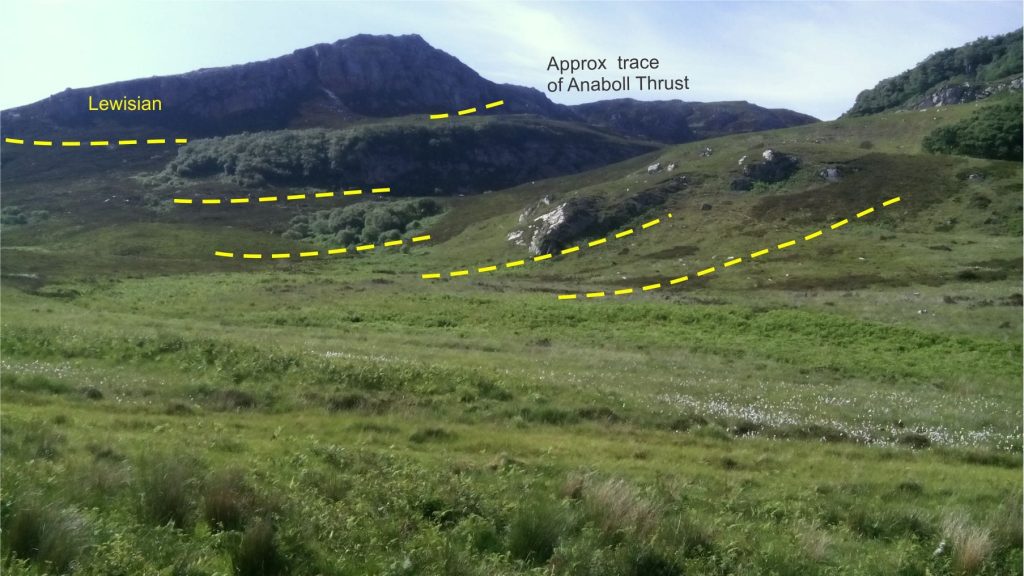
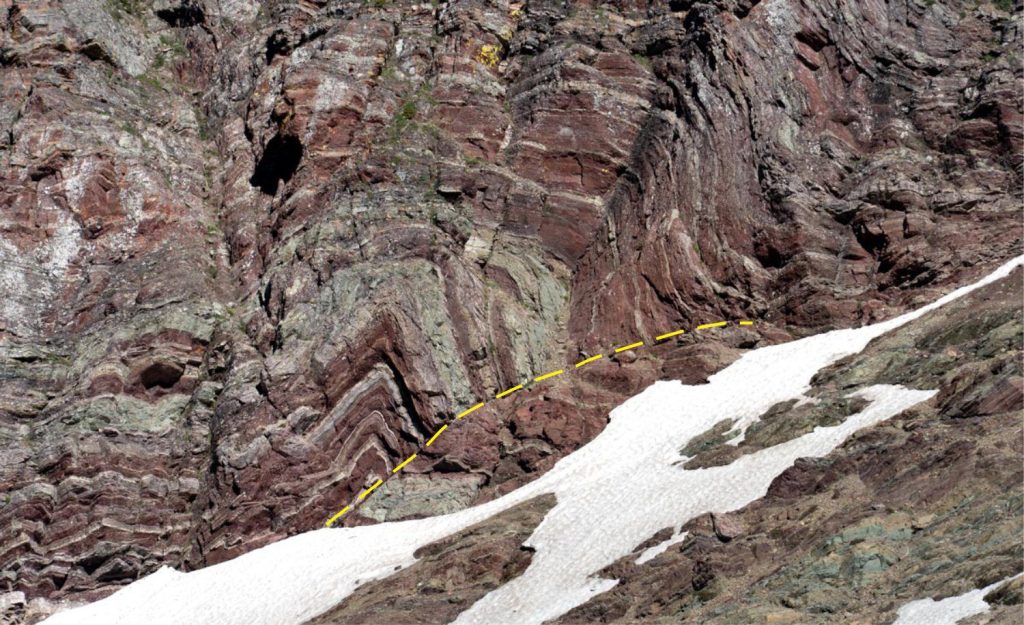
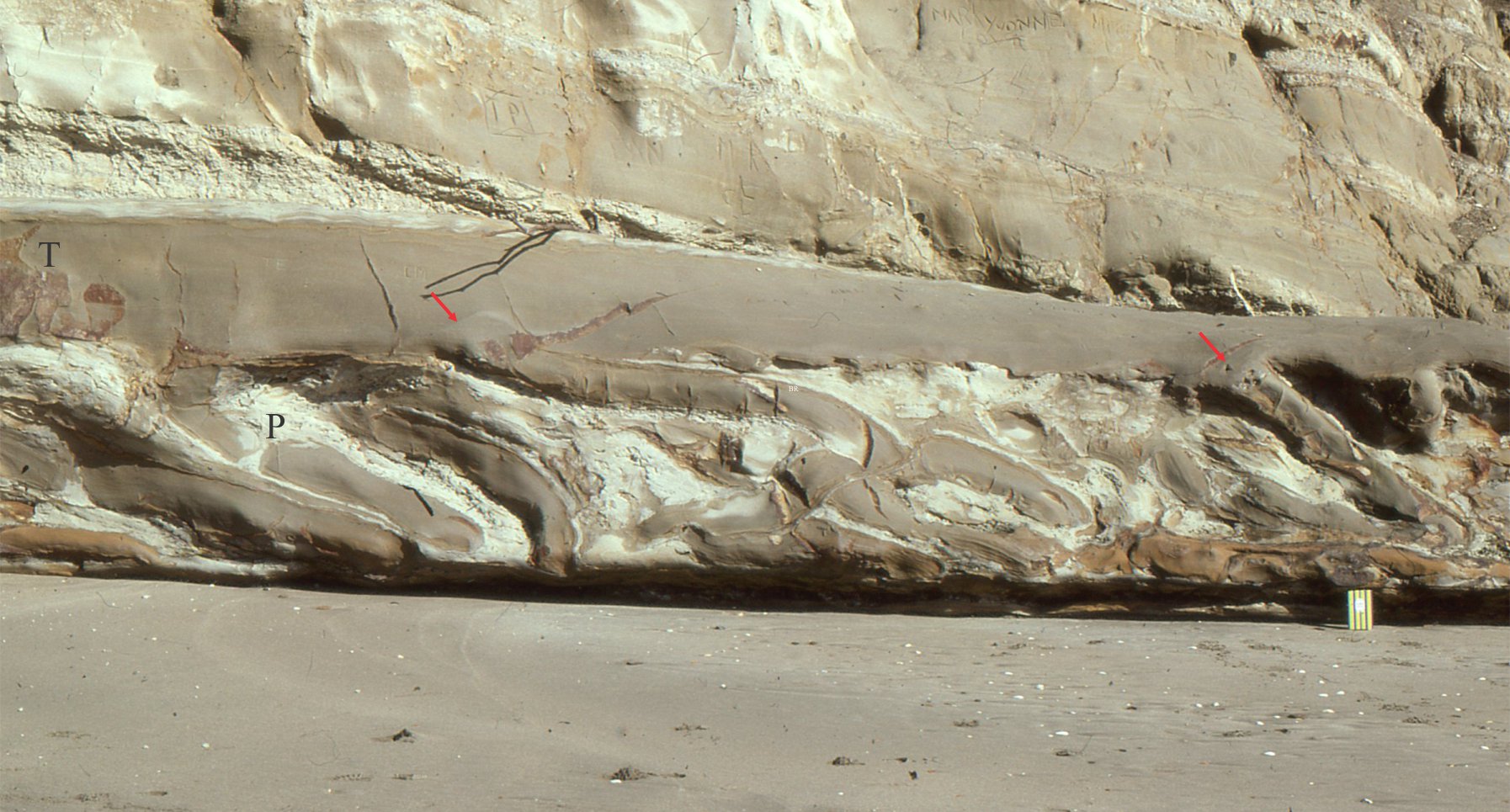
Fault propagation folds: Folding caused by the distribution of strain beyond a fault tip, as the thrust fault propagates. This mechanism also produces anticline-syncline pairs. A nice example from the tip of Lewis Thrust, Alberta Front Ranges, is shown below. The isoclinal fold pair in the header image (top of page) are also fault propagation folds.


Fault splay: A single fault strand divided into two or more faults such that displacement is distributed across the new structures.
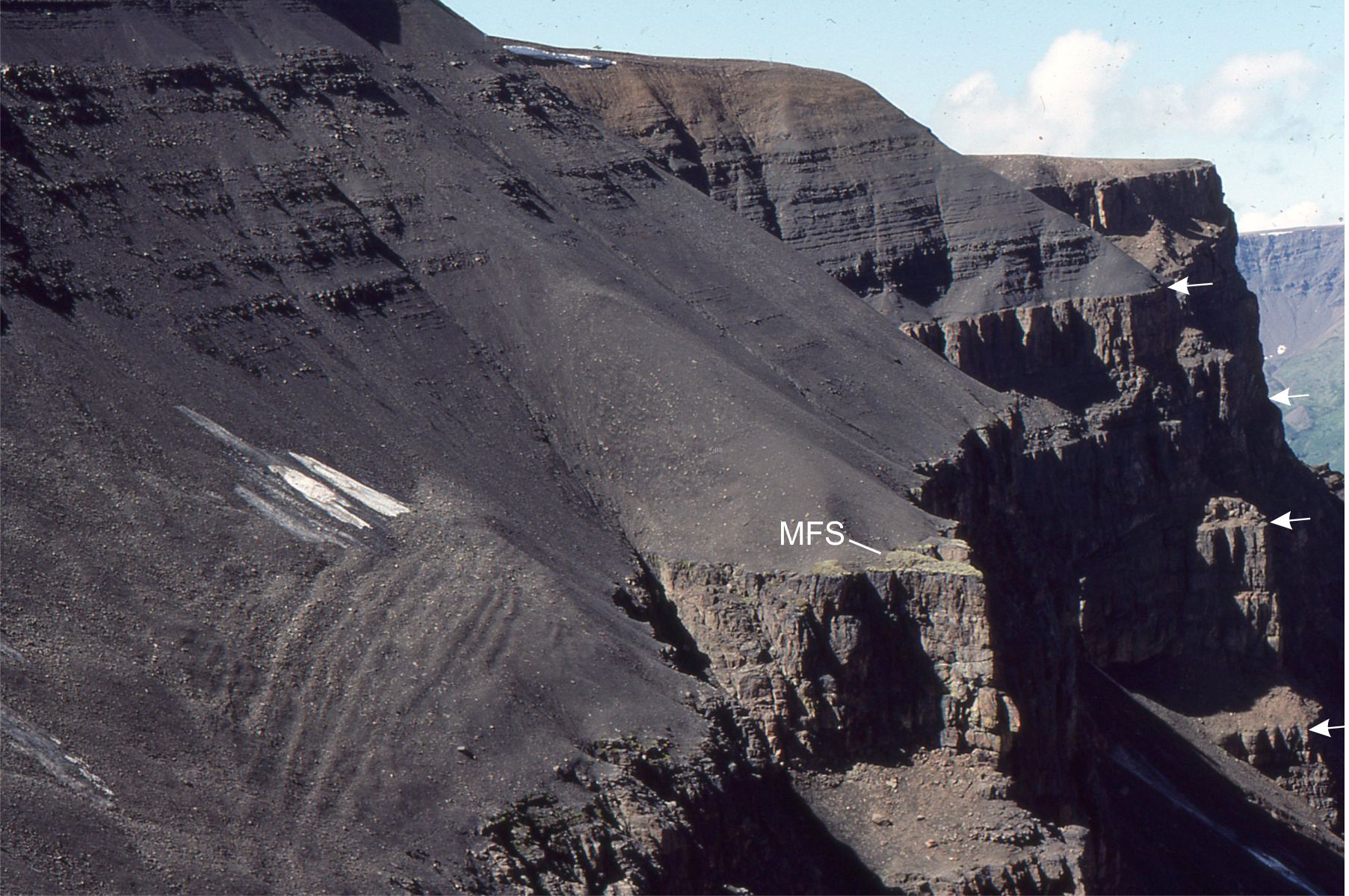
Fold-thrust belt: A major thrust system developed during lithosphere-scale plate convergence, with cumulative shortening of 100s of kilometres, that usually results in mountain building. The resulting topographic results in flexural and formation of a foreland basin. Thrust faults are generated in pre-existing strata, but usually evolve to include the proximal parts of the foreland basin and its sediments. An example is shown below.
Horse: A panel of rock bound on all sides by thrusts. Duplexes are a stack of horses.
Imbricate fan: Fan-like splay of thrust panels and thrust faults generated from a single décollement. Unlike duplexes, there is no roof thrust,
In sequence thrusts: In a system of thrusts, the most recent fault is at base of the thrust pile and most proximal to the foreland – propagation is towards the foreland. Older thrusts are stacked progressively hinterland-ward. In sequence thrusts place older rocks on younger as the fault propagates up the ramp through progressively younger strata. Cf. out of sequence thrusts.
Klippe: Plural = klippen. A remnant of a thrust panel or other allochthonous structure, isolated by erosion, that overlies and is surrounded by autochthonous rock. Cf. Window.
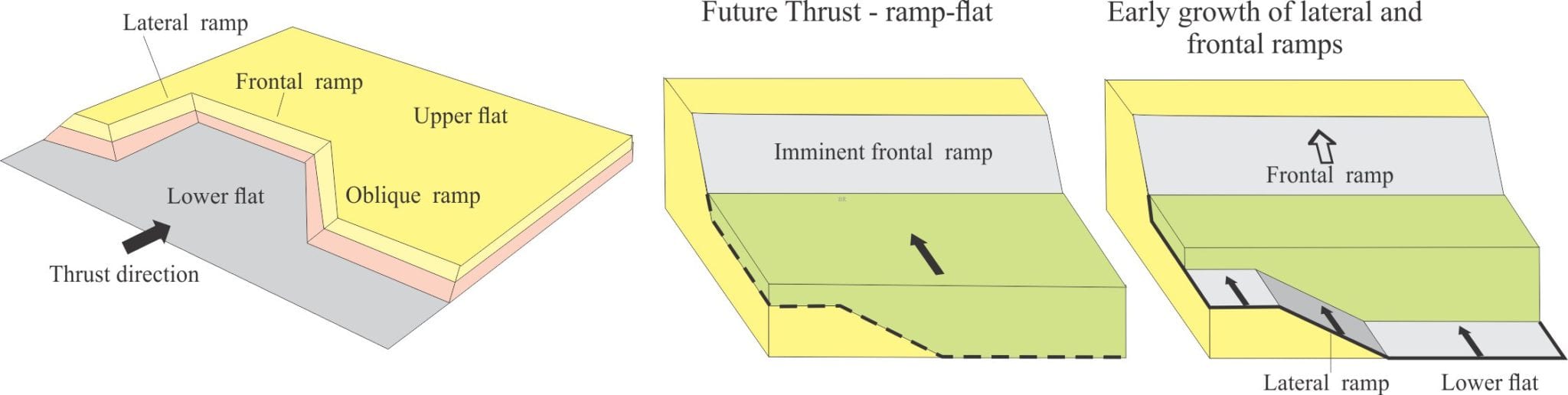
Lateral Ramps: Fault ramps at right angles or oblique to the strike of a thrust complex that transfer displacement from a lower to higher flat. Fault planes dip 10o to 30o. As shown in the diagram below, fault displacement across the ramp is basically strike-slip.
Out of sequence thrusts: Basically, thrusts that don’t conform to the normal in-sequence style. They commonly form in and cut across or reactivate older thrusts. They may place younger strata over older.
Passive roof thrust: A thrust that takes no part in displacement but develops passively during underthrusting or wedge insertion. Roof thrusts of triangle zones are commonly passive.
Roof-floor thrusts: Major thrusts providing the upper and lower boundary faults for duplexes. At the front of the duplex a roof thrust will step down and floor thrust step up to merge into a common zone of displacement.
Tear faults: Mainly strike-slip faults oriented at a high angle to a thrust fault, that accommodate bending and other discontinuities along the thrust, breaking it into compartments.
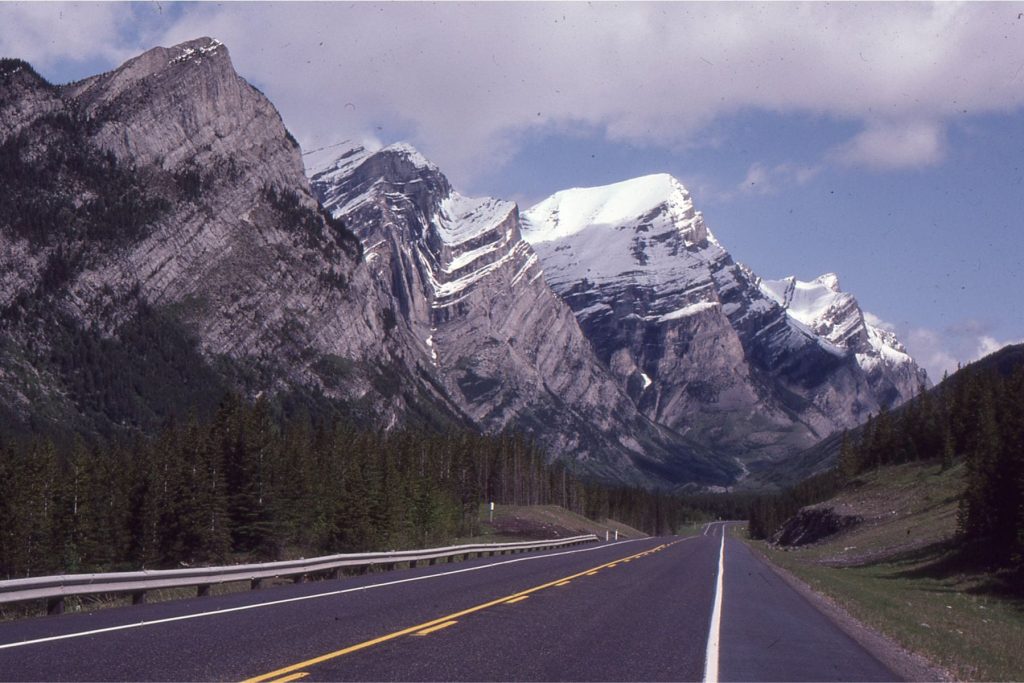
Thin-skinned deformation: A reference to crustal-scale deformation, such as fold-thrust belts, that structurally overlie basement rocks that have not been involved in the deformation. The cross-section shown below (Alberta Front Ranges) is a classic example. In that example, the fold-thrust belt is part of the allochthon, and the Paleozoic cratonic strata and crystalline basement are part of the autochthon.
Thrust flats: Initiation of thrust displacement begins along a mechanically weak layer, such as a shale; a bedding plane or foliation-parallel fault that has a hanging wall and a foot wall. Thrust flats are usually paired with ramps.
Thrust ramps: Thrust displacement is transferred from a flat to an inclined fault plane, or ramp that breaks through mechanically strong layers. Ramps commonly, dip at angles or 10 – 30 towards the hinterland; thus, vergence is toward the foreland. Ramps, like most faults, have hanging and foot walls. Cutoffs provide an opportunity to measure the amount of slip. Thrust ramps are usually paired with flats. Displacement is also accommodated by folds in the hanging wall.
Thrust tip – tip line: The point or fault plane edge where displacement ends. Note this does not mean that deformation also stops at these fault plane limits; strain is usually accommodated by folding, and in some cases cleavage.
Thrust vergence: The direction of hanging wall transport relative to the foot wall. In most fold-thrust belts and accretionary wedges vergence is towards the foreland.
Transfer zone: The location along a fault where displacement is transferred to a neighbouring fault. Thus, displacement along the initial fault dies out, and its neighbour takes up the strain.
Triangle zone: In a foreland fold-thrust belt context, it defines a wedge-shaped, subsurface deformation front having a basal thrust (the main décollement) and a hinterland-dipping roof thrust. The roof thrust is commonly passive.
Window: A look through an (allochthonous) thrust sheet into the underlying autochthon.
Thanks to Dr Sandra McLaren, Melbourne University for permission to use the sand-box experiment images. Check out her Twitter page @sandramcgeo
Other posts in this series on Common Structure and Mapping Problems
Solving the three-point problem
Stereographic projection – the basics
Stereographic projection of linear measurements
Stereographic projection – unfolding folds
Stereographic projection – poles to planes
The Rule of Vs in geological mapping
Using S and Z folds to decipher large-scale structures
Cleavage and cleavage-bedding intersections
The kinematics of deformed rock










1 thought on “Thrust faults: Some common terminology”
Very good summary. Clearly explained Thrust concept and field evidences. Many Thanks