The Origin of Life? – Science persists in asking…
Galileo Before the Holy Office Joseph Nicolas Robert-Fleury
When our Renaissance heroes Galileo, Copernicus, and Tycho Brahe cogitated the celestial sphere and removed humanity from the centre of the physical universe, they must have developed cricks in their necks – regularly looking over their shoulders for the ever-watchful ecclesiastical authorities who brutally insisted on maintaining the status quo. Six hundred years later we still want to understand the unknown and persist in our curiosity, although the consequences of our enquiry are not usually as dire as those faced by Copernicus. We continue to ask questions and one of these, for which there are still few answers, is ‘how did life begin?’. Embedded in a question like this are metaphysical quandaries that consider consciousness and our humanity; one wonders whether such attributes will ever enter the realm of the empirical. However, science can attempt to deal with explicitly empirical parts of the question, such as ‘how might organic molecules, that are critical to functioning cells, have formed on the ancient earth?’.
The first article on this thorny topic dealt with an iconic set of chemical experiments conducted in the early 1950s. This post takes these experiments incrementally further.
 In 1953 Stanley Miller, then a young postgraduate student under the tutelage of Harold Urey, conducted experiments that produced several organic compounds, including amino acids. The chemical reactions were all abiotic. They demonstrated that some of the important chemical ingredients of living cells could be produced without the interaction of life-forms. This was a huge step forward in scientists’ understanding of how life arose on earth.
In 1953 Stanley Miller, then a young postgraduate student under the tutelage of Harold Urey, conducted experiments that produced several organic compounds, including amino acids. The chemical reactions were all abiotic. They demonstrated that some of the important chemical ingredients of living cells could be produced without the interaction of life-forms. This was a huge step forward in scientists’ understanding of how life arose on earth.
However…
it was later discovered that there were problems with some of the original experimental conditions:
“We now know that the earliest atmosphere on earth did not contain abundant ammonia and methane (that Miller had used in his experiments), but mostly carbon dioxide, water and nitrogen. When Miller repeated his experiments in 1983 using these new ingredients, the results were pretty disappointing – a few simple organic compounds but no amino acids.”
Enter Jeffrey Bada, about 50 years later. Bada was intrigued by his mentor Miller’s ideas, that experimentation could help to solve some of the riddles of the Origin of Life. Bada discovered the reason why Miller’s 1983 experiments failed to produce amino acids. Compounds called nitrites (NO2–) were also formed.
Most of us have had exposure to nitrites – literally. They are commonly used as preservatives in processed food.
The nitrites produced in Bada’s (and Miller’s) experiments did the same kind of thing that they do in food – they destroyed the amino acids. So Bada added some other compounds to the experimental mixture to neutralise the nitrites – in the ancient natural world this would have been accomplished by the abundant carbonate (CO3) and iron (Fe) in ancient seawater. And bingo! Lots of amino acids (and other compounds). The Miller-Urey concept had been resurrected.
So much for controlled lab experiments. What would a natural laboratory have looked like, out there in the ancient atmosphere and oceans, that might have produced these kinds of compounds? Jeffery Bada, in an interview suggested
“You can imagine early Earth being covered by hundreds of these volcanic islands, acting as little prebiotic factories. All of them would be contributing to the prebiotic soup. I think this demonstrates that the idea of making compounds directly on the early Earth via processes that Miller imagines in 1953 is still very much relevant today.”
A different environment; a different set of experiments
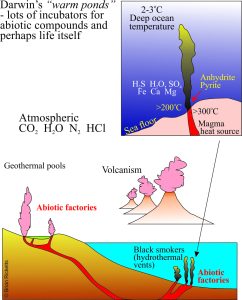
An article in a 2010 issue of Smithsonian Magazine by Helen Fields gives us a great lead-in to a different kind of experiment. The article describes how Bob Hazen, a mineralogist at the Carnegie Institution for Science was working in the 1990s on hydrothermal vents (or black smokers) in the deep oceans. Vents like these, observed by deep submersibles often have strange rock chimneys that harbour some pretty weird marine worms, shell fish and other strange critters in waters 100s of metres deep. The formations vent superheated water and steam (more than 300oC) at very high pressures. While the vents are a fascinating study in themselves, Hazen hit on the idea that 4 billion years ago (no animal life back then) vents like these may have provided the right environment for chemical reactions that eventually gave rise to living cells – a bit like Charles Darwin’s “…warm pond…”.
Being a mineralogist by trade, Hazen and his colleagues developed some experiments where simple organic compounds (including nitrogen and ammonia) were placed into small sealed tubes made of gold capable of withstanding high pressures and temperatures (gold was used because it is inert). The resulting products included a large numbers of organic compounds including amino acids and sugars.
 Miller and Bada succeeded in making similar compounds using simulated lightning. Hazen’s energy source was in the oceans themselves. We can extend Hazen’s idea to geothermal systems like those we see today in New Zealand, Chile and Iceland, where heat, water and dissolved minerals may have come together as small incubators. The vents are perhaps a bit like what Bada envisioned as “… little prebiotic factories.”
Miller and Bada succeeded in making similar compounds using simulated lightning. Hazen’s energy source was in the oceans themselves. We can extend Hazen’s idea to geothermal systems like those we see today in New Zealand, Chile and Iceland, where heat, water and dissolved minerals may have come together as small incubators. The vents are perhaps a bit like what Bada envisioned as “… little prebiotic factories.”
Science is still a long way from solving the Origin of Life puzzle. More recent experiments have involved detailed study of the structure of amino acids, the ways in which proteins group together, and whether complexes like RNA (one of the fundamental building blocks of cells) are also involved in the formation of compounds that make up the fabric of cellular life. Another recent experiment attempted to mimic the ocean composition (about 4 billion years ago) and showed that the ancient iron-rich oceans themselves may have catalyzed (promoted) certain reactions involving complex sugars and phosphates that are important intermediaries in cell metabolism. The actual chemistry of experiments like these is not for the faint hearted; they have progressed from the relatively simple Miller-Urey experiments, to attempted reconstruction of metabolic pathways and other cell functions. All of these enquiries bring us just a little closer to understanding one of life’s great mysteries