An introduction to common stratigraphic and sedimentological tasks, and some basic theory


Posts here present an introduction to common stratigraphic and sedimentological tasks, such as recognizing and measuring sedimentary structures and stratigraphic sections in the field, describing sediments and sedimentary rocks, and the basic principles of sedimentation.
See also the companion page structural geology and mapping
Determining stratigraphic tops
Measuring a stratigraphic section
Identifying paleocurrent indicators
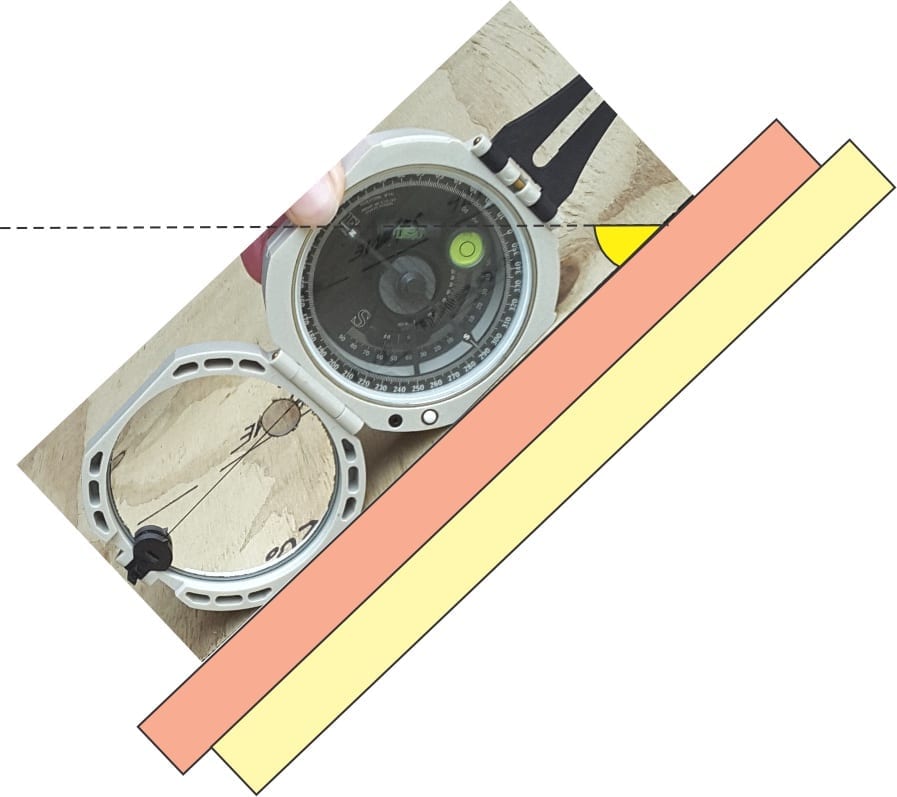
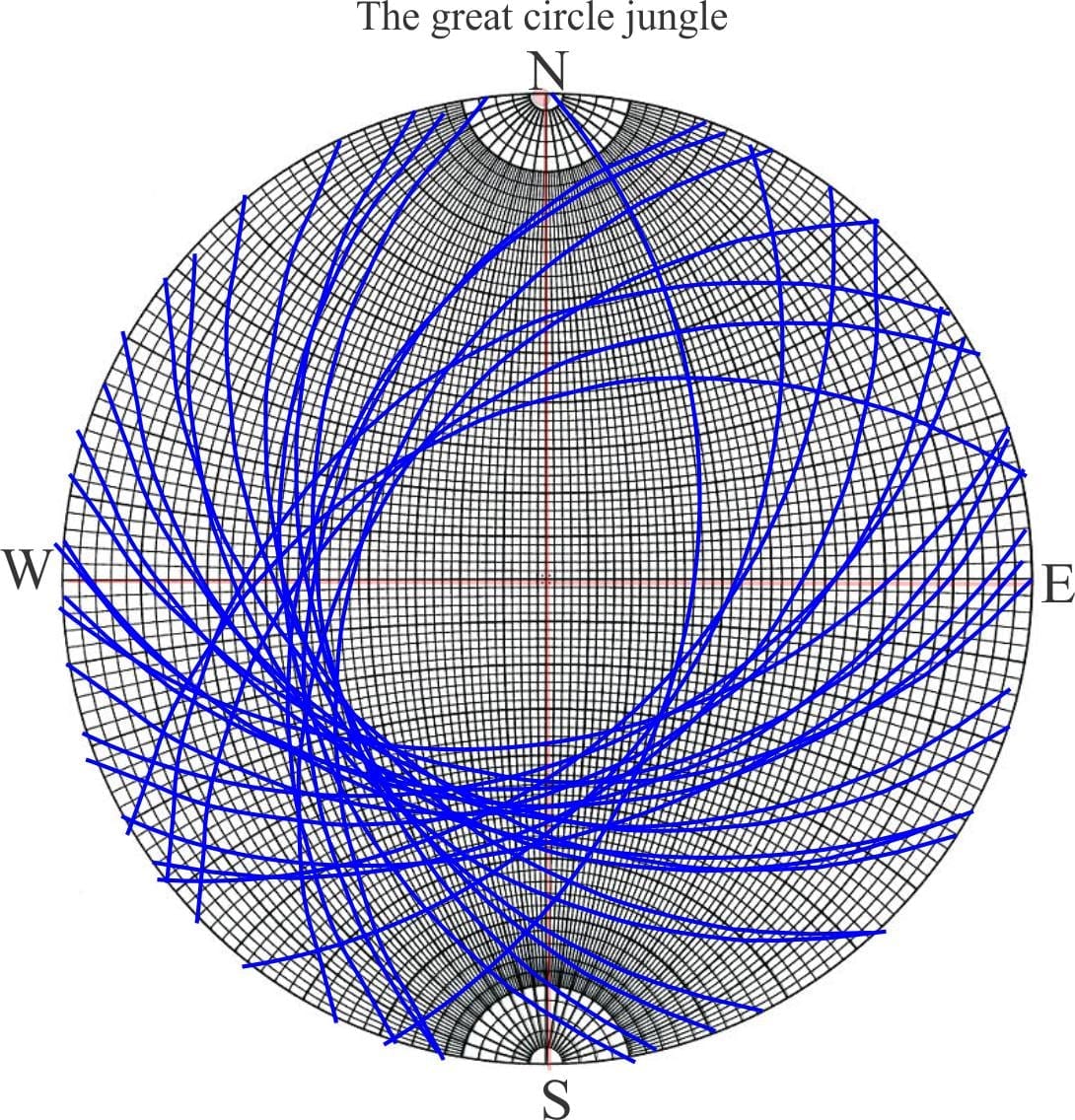
Measuring and representing paleocurrents
Crossbedding – some common terminology
The hydraulics of sedimentation: Flow Regime
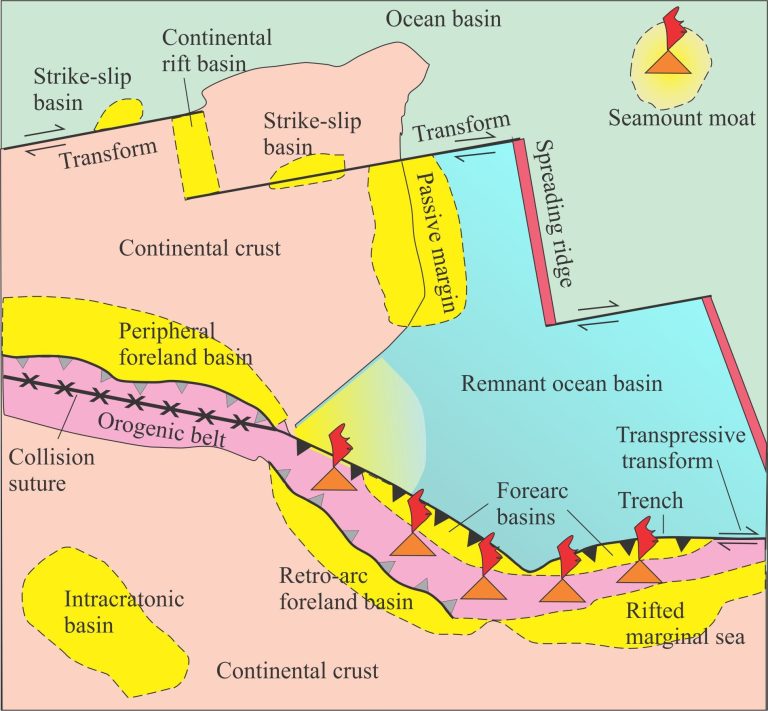
How do we identify a basin margin?
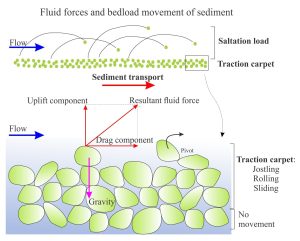
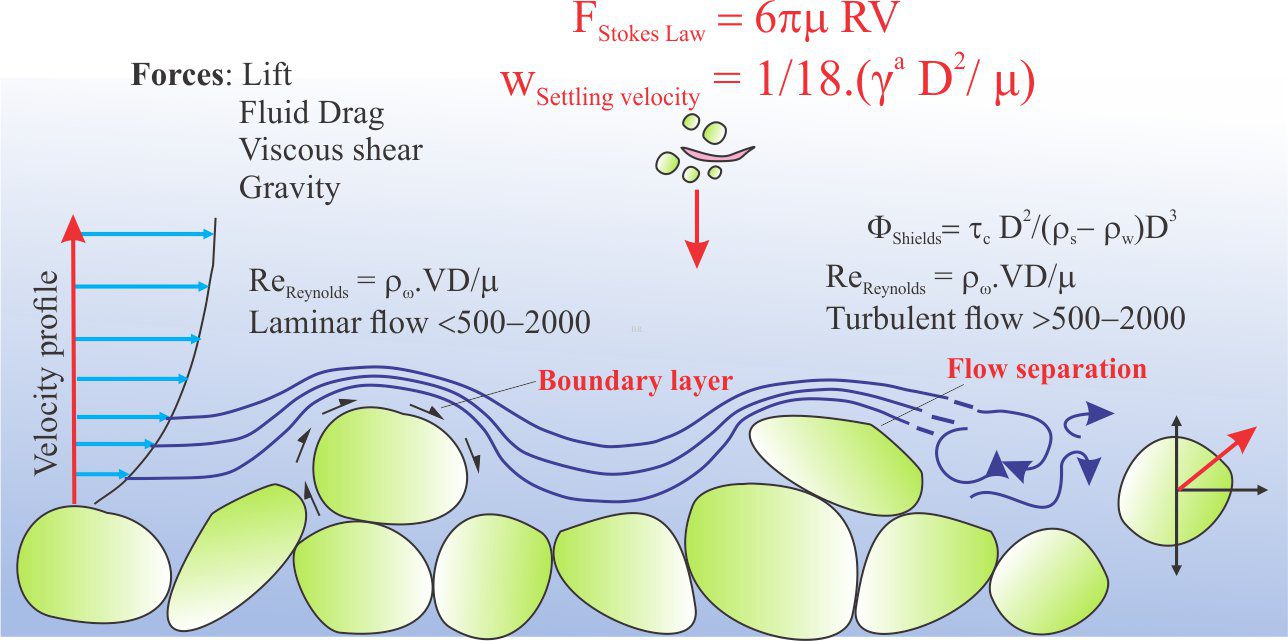
Sediment transport: Bedload and suspension load
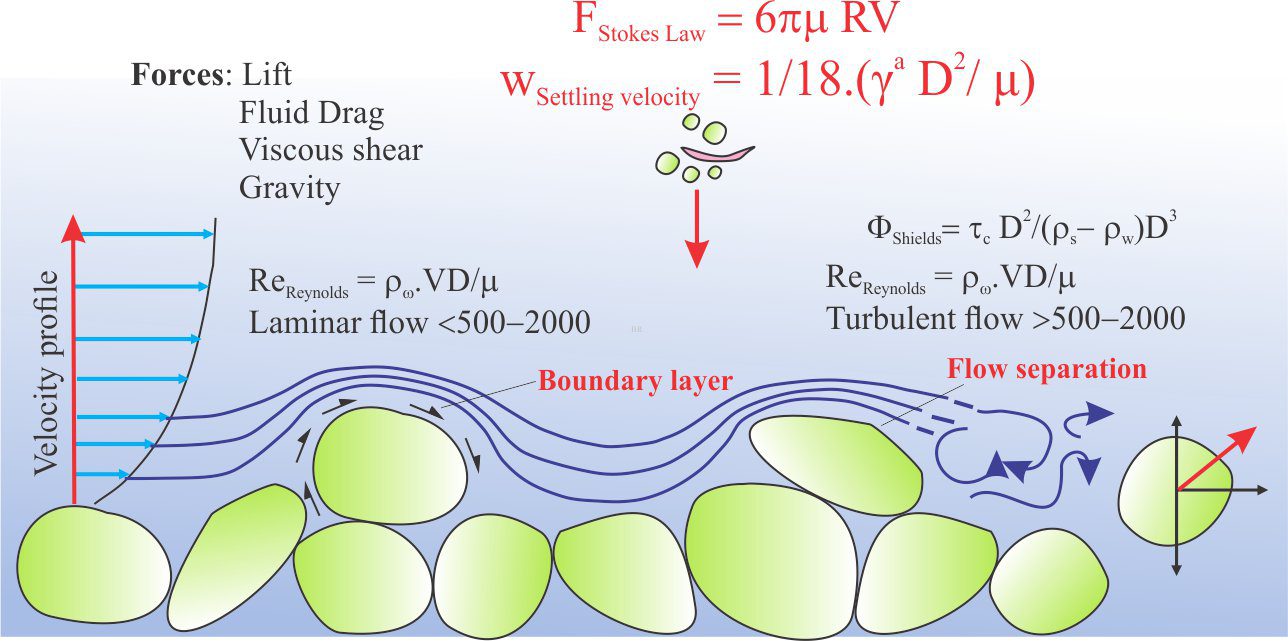
Fluid flow: Froude and Reynolds numbers
Fluid flow: Shields and Hjulström diagrams
Fluid flow: Stokes Law and particle settling
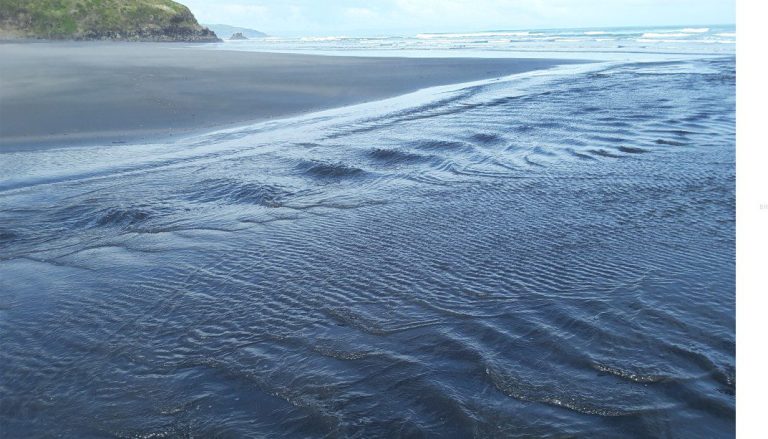
Beach microcosms as fan delta analogues
Soft sediment deformation
Rheology of soft sediment deformation
Invertebrate morphology for sedimentologists
Bivalve morphology for sedimentologists
Trilobite morphology for sedimentologists
Gastropod shell morphology for sedimentologists
Cephalopod morphology for sedimentologists
Brachiopod morphology for sedimentologists
Echinoderm morphology for sedimentologists
Coral morphology for sedimentologists
Graptolite morphology for sedimentologists
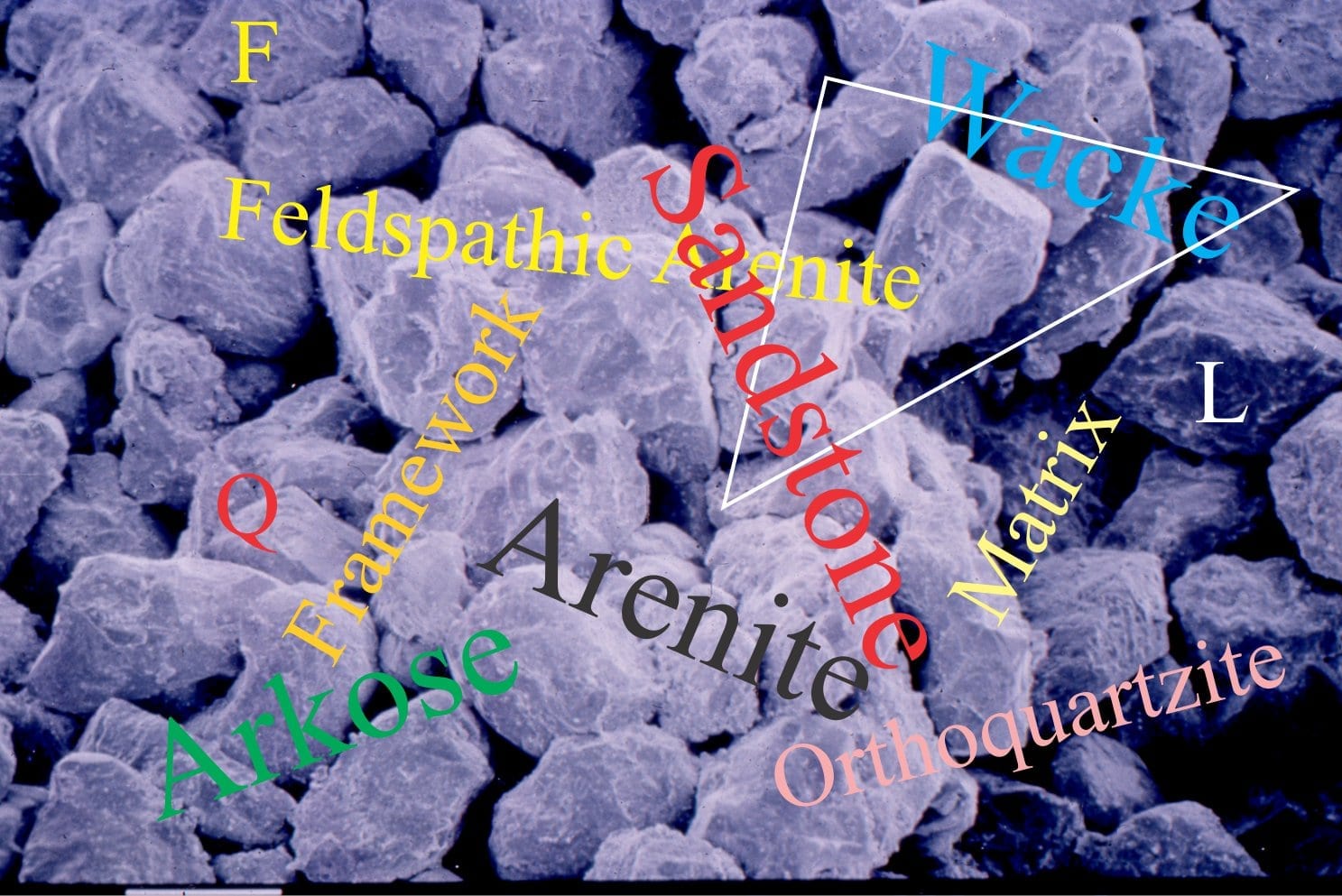
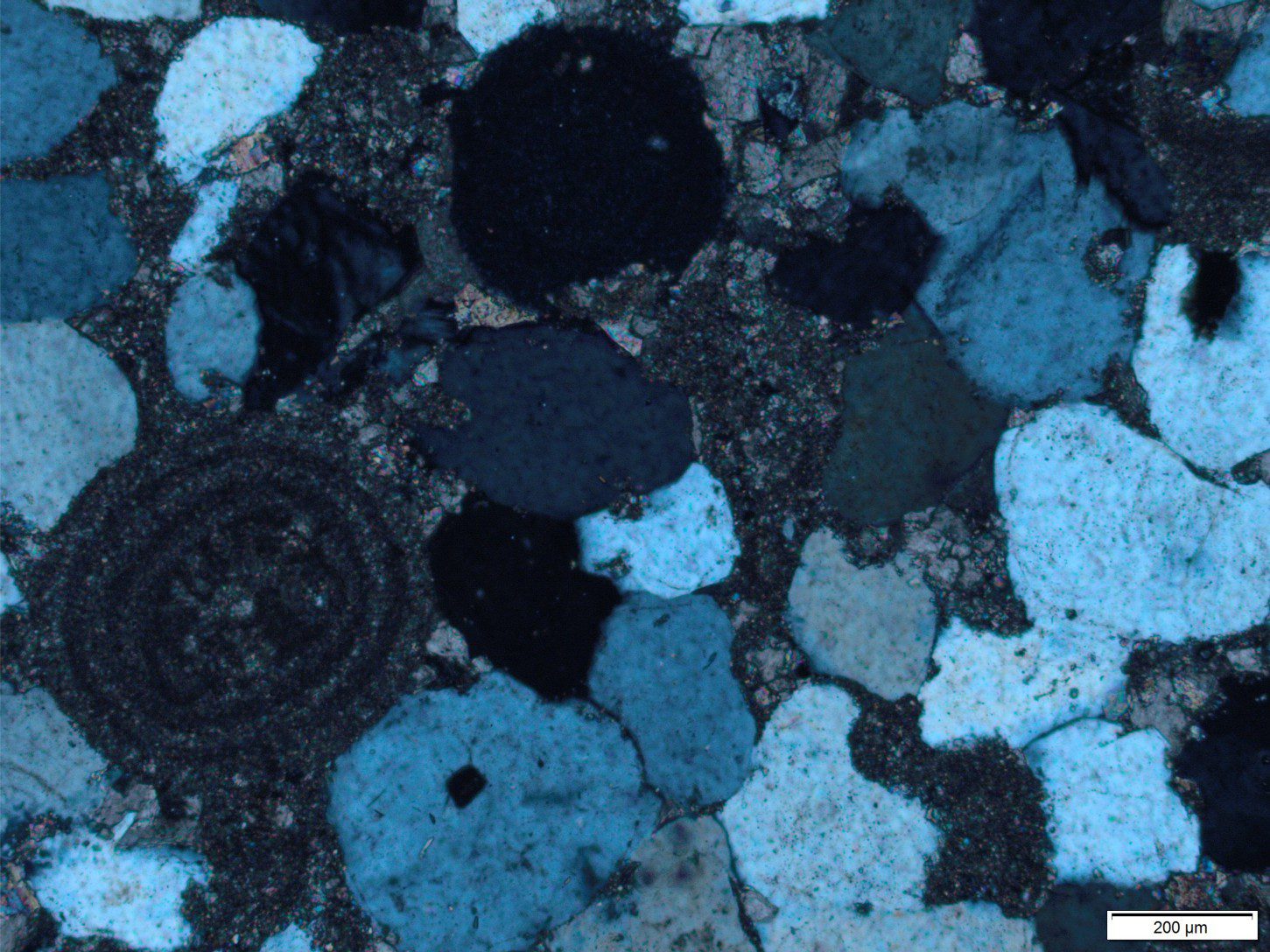
Sandstone lithofacies
Sedimentary lithofacies – An introduction
Ripple lithofacies: Ubiquitous bedforms
Ripple lithofacies influenced by tides
Tabular and trough crossbed lithofacies
Laminated sandstone lithofacies
Low-angle crossbedded sandstone
Hummocky and swaley cross-stratification
Lithofacies beyond supercritical antidunes
Subaqueous dunes influenced by tides
The three pycnals: Hypo-, homo-, and hyper
Storms and storm surges: Forces at play
Evolving tempestite lithofacies models
Gravel lithofacies
Introducing coarse-grained lithofacies
Crossbedded gravel lithofacies
The lithofacies of mountain streams
Three posts on tempestites:
3 Evolving tempestite lithofacies models
2 Storm surges and tempestites
1 Storms and storm surges: Forces at play
Seagrass, mangrove, and salt marsh lithofacies
Seagrass meadows and ecosystems
Seagrass lithofacies in the rock record
Geological models
Geological models: An introduction
Model dimensions and dimensional analysis
Analogue models of faults: scaling the materials
Self-organization, autocyclicity, and the rock record
Experiments with turbidity currents – some historical context
Experiments with turbidity currents – scaling laws
Experiments with turbidity currents – three examples
You might also want to check out …
A time-line for the first 4.6 billion years
Interpreting the ancient Earth