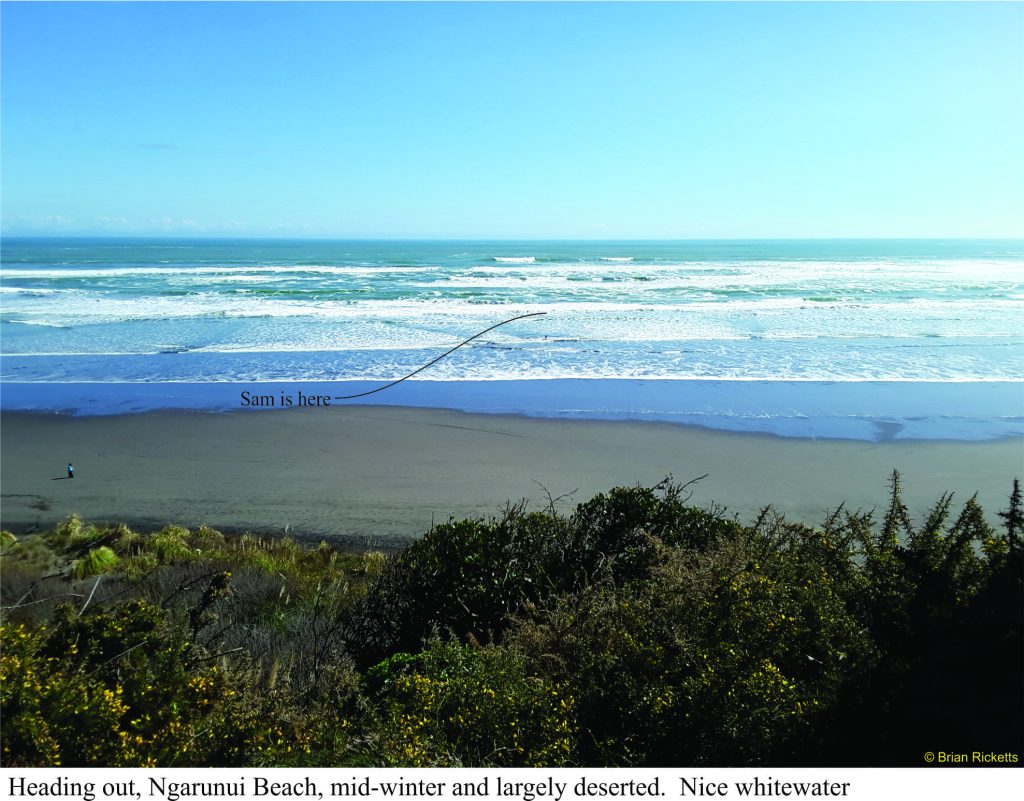
Sam had the day off so the two of us headed to Raglan and Ngarunui Beach, a typical wild, west coast North Island beach that includes a world class left-hand surf break at Manu Bay.
 Recipe; play boat in the truck, and a mid-winter sun, a balmy 20oC, cloudless, zephyrs. From the top of the hill that leads down to the main beach, there’s a great view of far off 3-4m swells, the wave build-up and final cascade as the foamy brine rushes towards the beach. The inner surf was a bit broken but there was enough blue-green water to satisfy even Sam.
Recipe; play boat in the truck, and a mid-winter sun, a balmy 20oC, cloudless, zephyrs. From the top of the hill that leads down to the main beach, there’s a great view of far off 3-4m swells, the wave build-up and final cascade as the foamy brine rushes towards the beach. The inner surf was a bit broken but there was enough blue-green water to satisfy even Sam.
Today there are some decent rip-currents plus a steady southward drift towards rocks at the south end of the beach. The rocks are pretty interesting, but not from a kayaker’s (or surfer’s) perspective of being dashed upon them.
Launching one’s boat is interesting to watch. Basically you get into your kayak in water that is ankle deep, fasten the deck and await the next wave for the pick-up and seaward drift. As you head out to cleaner water, there’s ample opportunity to limber up with a few rolls in the broken surf. There’s also plenty of scope for cartwheels, intentional or otherwise, or being pummelled in the wave breaks.
As for the rocks!
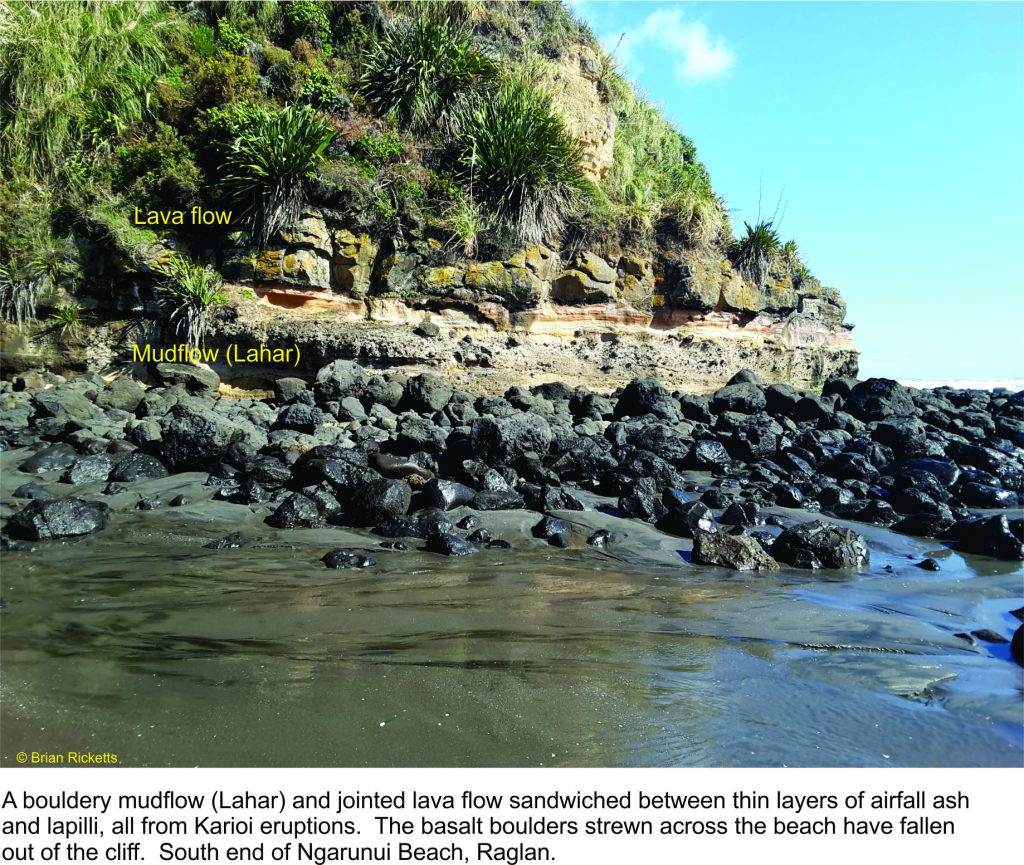
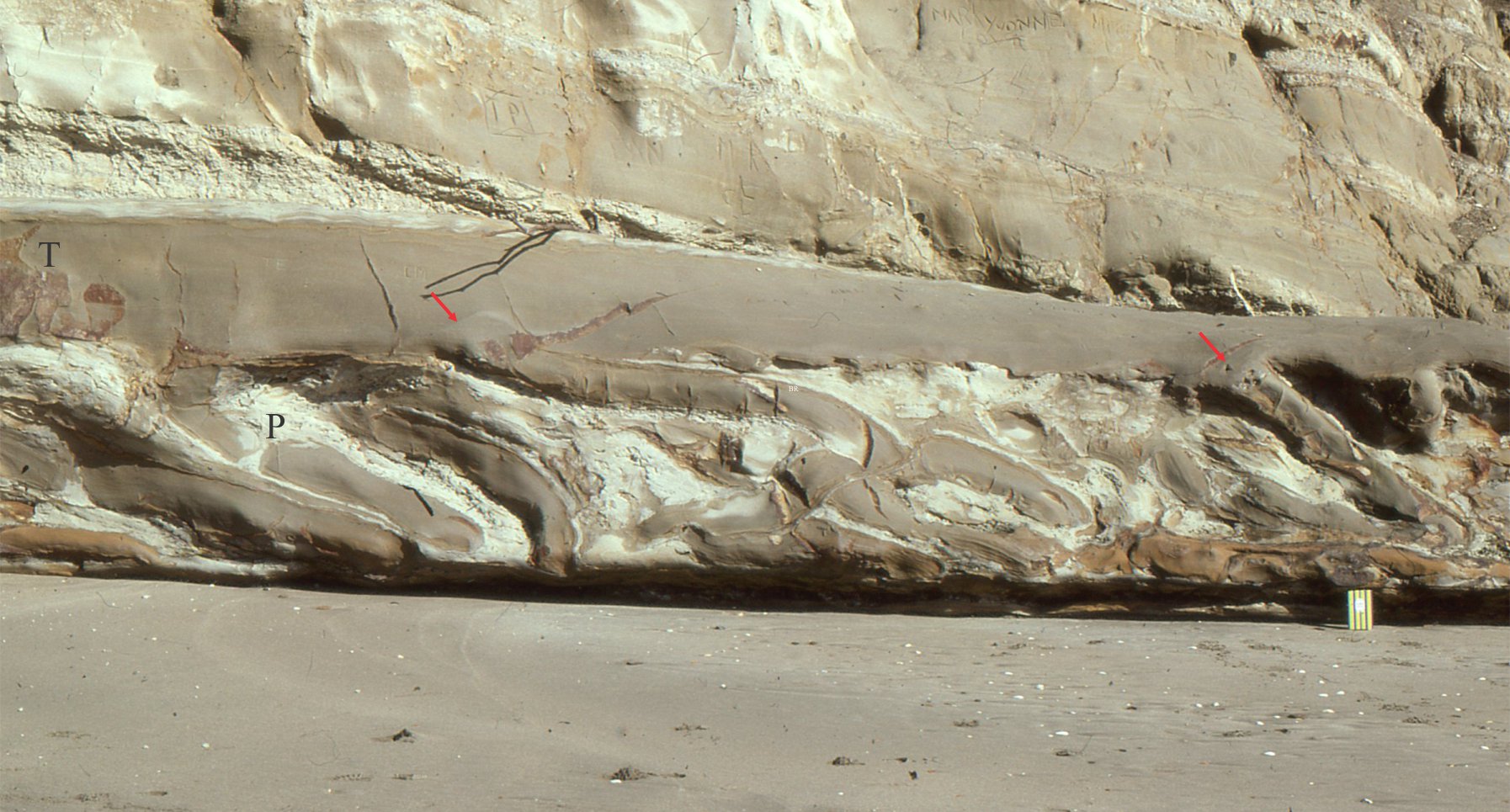
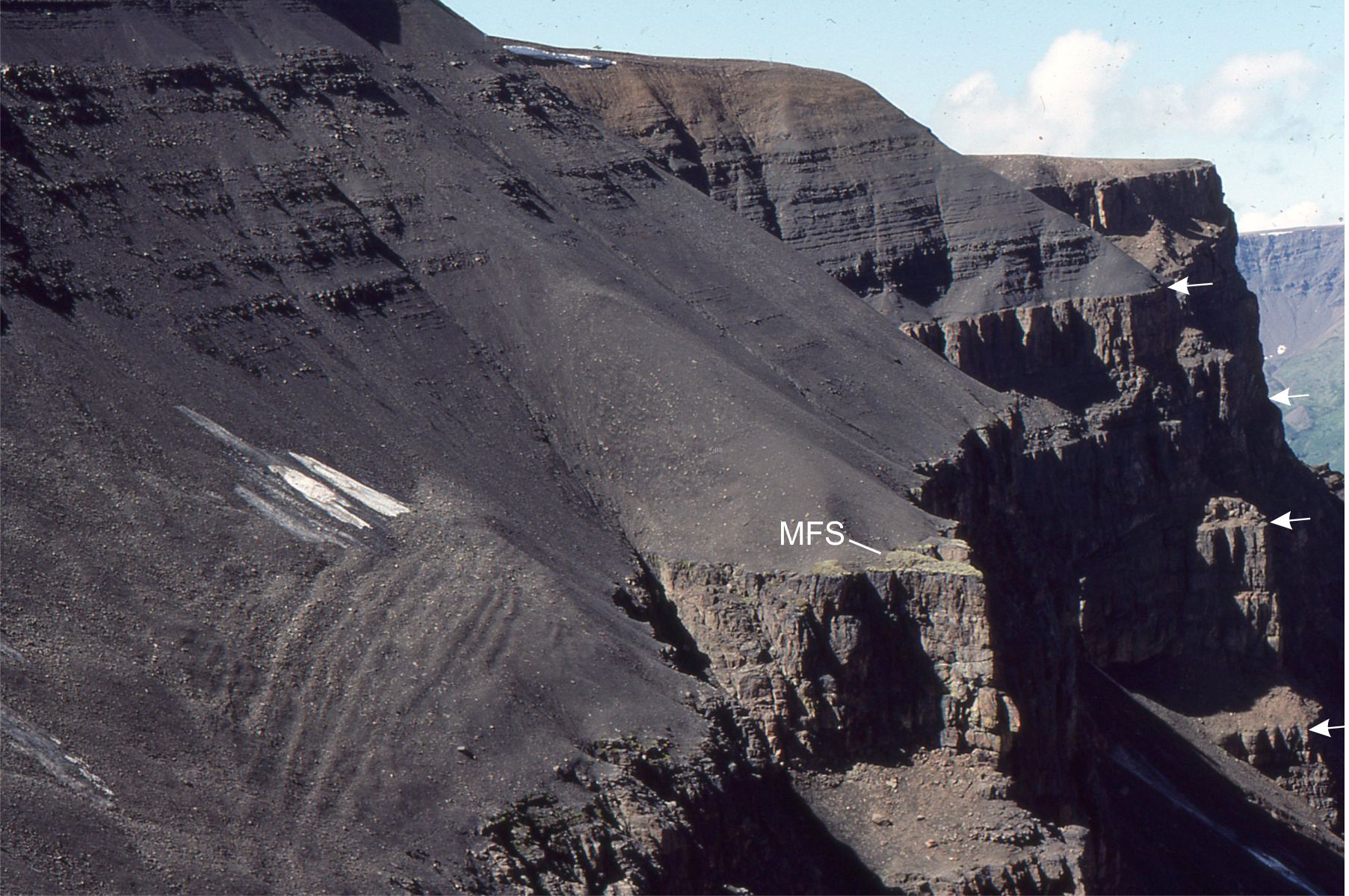
Raglan town and Ngarunui beach rest in the shadow of an ancient volcano; Mt. Karioi that, translated from Maori means to loiter, or stand by idly. This is a nice expression of an extinct volcano about 2.4 million years old, that in its hay-day was a regular eruptive ragamuffin but now just sits and watches. Cliffs at the south end of the beach contain deposits of volcanic ash and lapilli that once rained down on the surrounding area, plus bouldery mudflows, or lahars, that were probably pretty destructive. A few fossil sea shells are caught up in some of the volcanic sediments indicating that the shoreline 2.4 million years ago may have lapped upon its outer flanks.
Karioi is one of four volcanoes (the others are Pirongia, Kakapuku, and Te Kawa) that all erupted over a period lasting from 3.7 to 1.8 million years (Te Kawa is the youngest). Erupted lavas were mostly basalts. Karioi’s original volcanic edifice of can still be recognised but it has been eroded into steep ridges and ravines, that now are clad in native forest. The south side of the volcano can also be accessed from Ruapuke Beach.
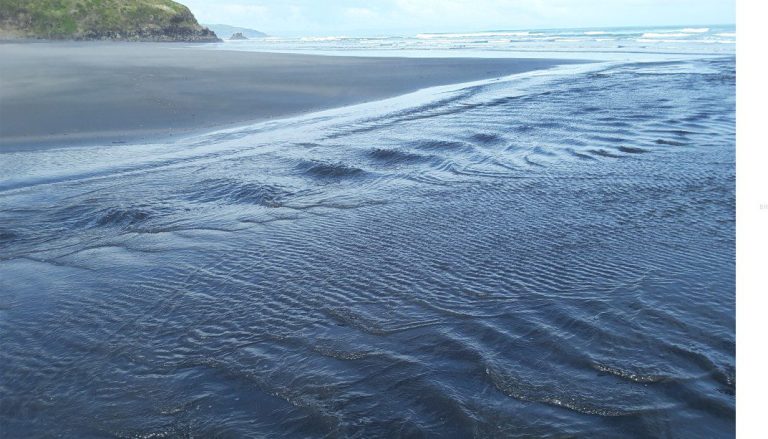
The beach at Ngarunui has black sand, or iron-sand like many west coast North Island beaches. Sand here consists mostly of the iron-bearing mineral titanomagnetite (a titanium-bearing form of magnetite – magnetite itself is an iron oxide), plus a few other dark green or black minerals like hornblende and pyroxene, that likely originated from volcanoes on Taranaki Peninsula, about 120km to the south. The Taranaki volcanoes were eroded and the resulting iron-bearing sands distributed north and south along the shore and continental shelf. In summer, the dry sands become very hot, as anyone lacking appropriate footwear will attest to (even second-degree burns). The iron-sands have been used locally to produce steel.
Raglan Area School is the only high school in New Zealand to have a Surf Academy.












2 thoughts on “Class 5; Surf rolls and cartwheels; Surf kayaking at Raglan, New Zealand”
The world has many wonders, just by looking to its beauty and the different formation of the rocks here in Raglan and Ngarunui beach, where happiness and adventure awaits with its beautiful scenery and having a fresh environment. A good place where family bonding is a must.
This unique color of sand is very impressive for every tourist who gets there.