This category of Atlas images, is not intended as a comprehensive outline or set of definitions of sequence stratigraphy, but rather field examples of strata, stratigraphic trends (an essential component of systems tracts), and stratigraphic surfaces. There are many excellent journal papers, text books, and conference short courses devoted to sequence stratigraphy, so consult them if needs be.
The link to Sequence Stratigraphic Principles will take you to more descriptive posts.
The Atlas of Unconformities also has additional examples of sequence boundaries
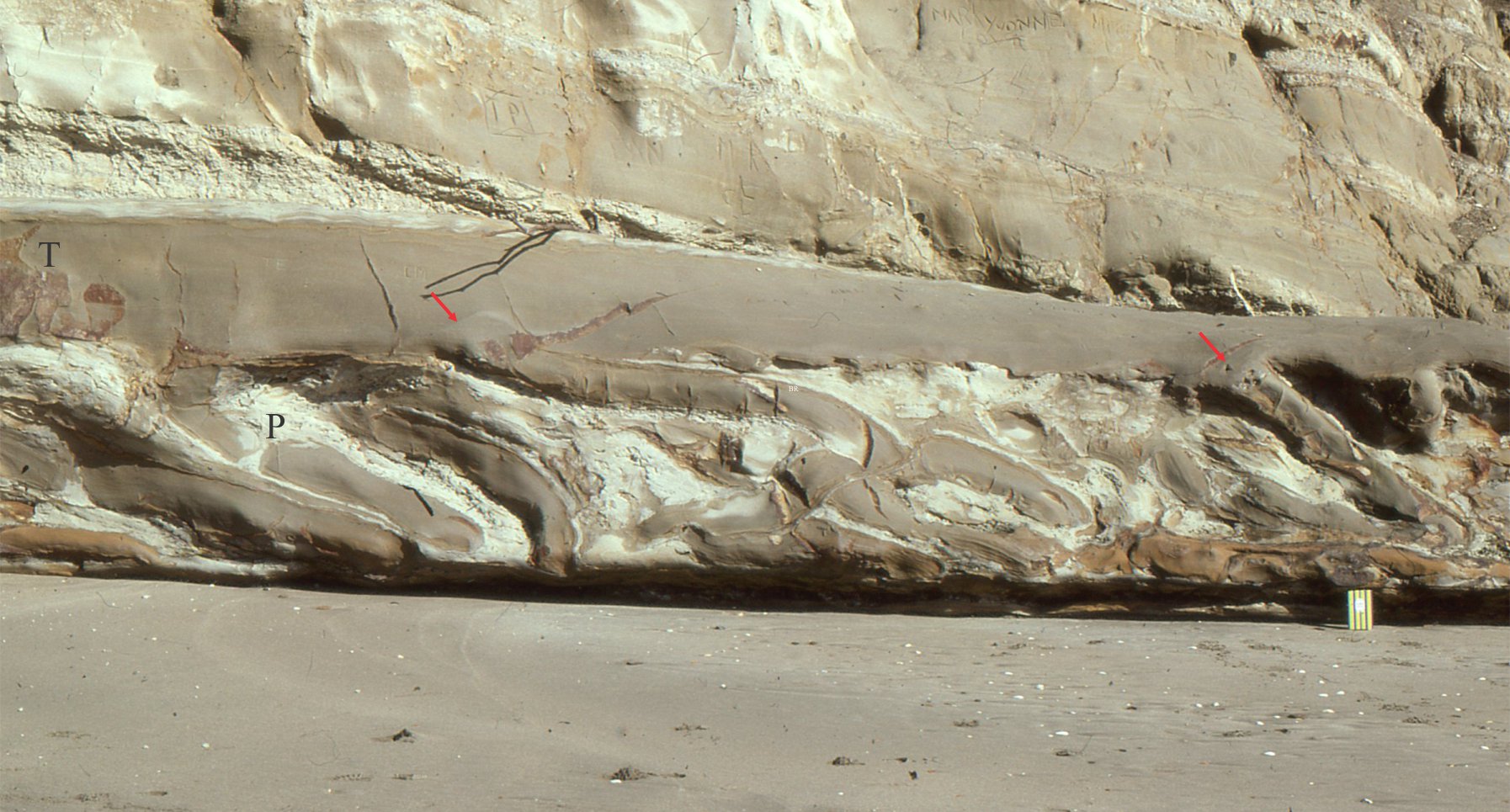
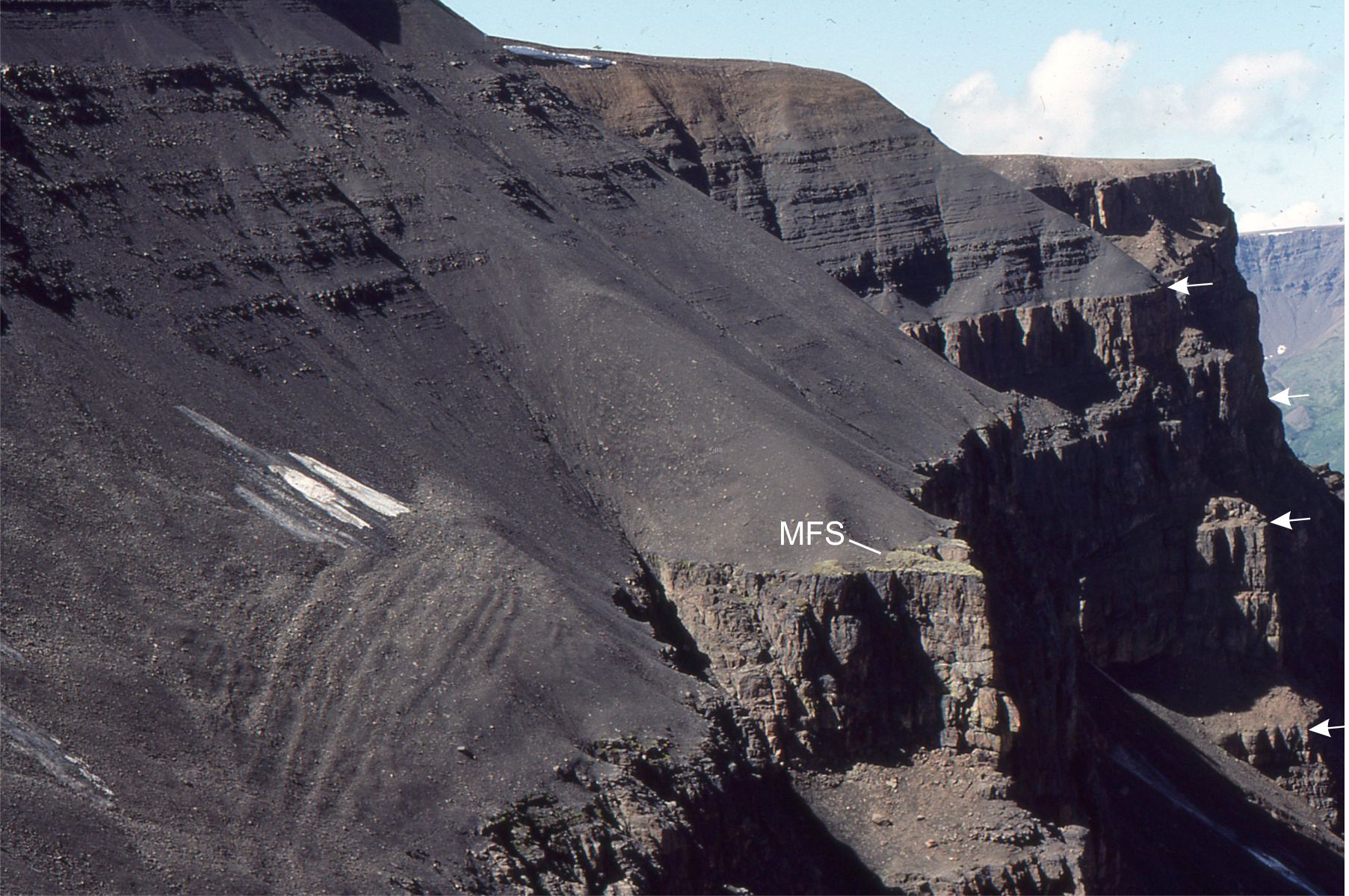
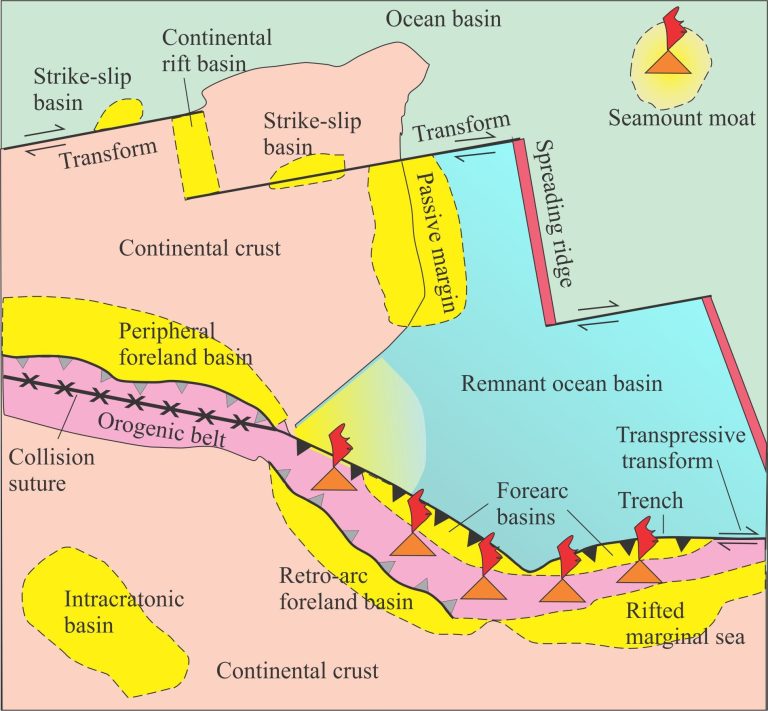
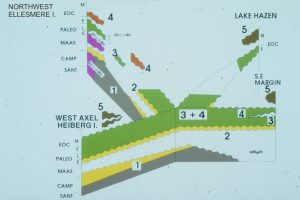
Some key sequence stratigraphic components illustrated here include (abbreviations on the images):
HST Highstand Systems Tract (progradational-aggradational) overlies the MFS and underlies the erosion surface formed during the FSST)
FSST Falling Stage Systems Tract (forced regression and progradation during relative sea-level fall)
LST Lowstand systems tract (now restricted to end of relative sea-level fall and beginning of sea-level rise)
TST Transgressive Systems Tract (above the transgressive surface; Retrogradational onlapping during rising relative sea-level and low sedimentation rates. Condensed stratigraphy).
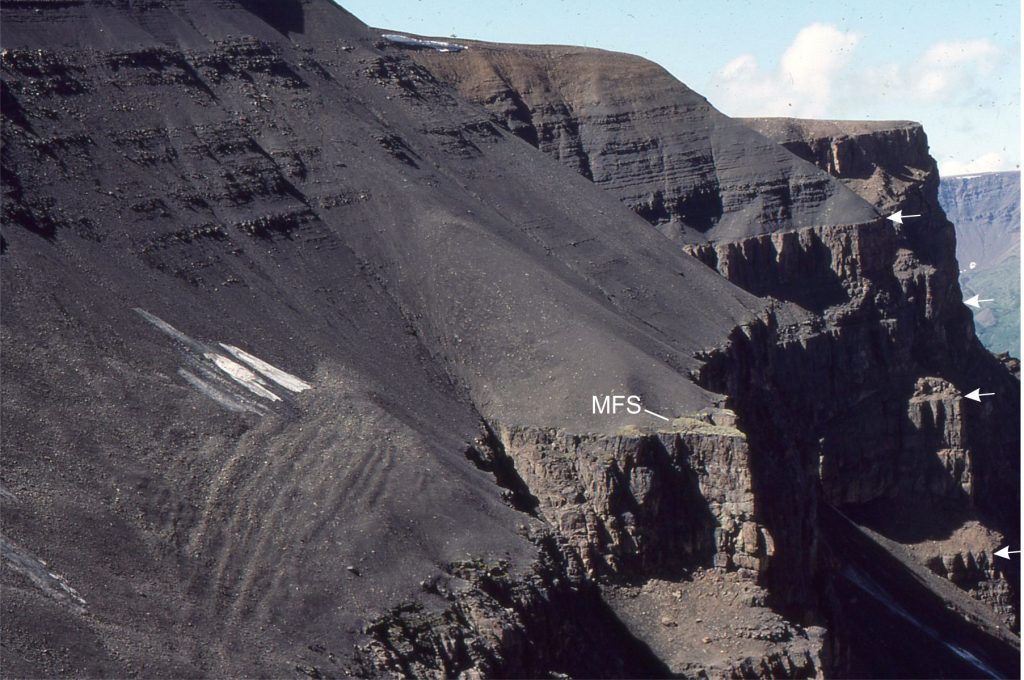
MSF Maximum Flood Surface (at the transition to sedimentation rates greater than creation of accommodation space. Also the base of the HST).
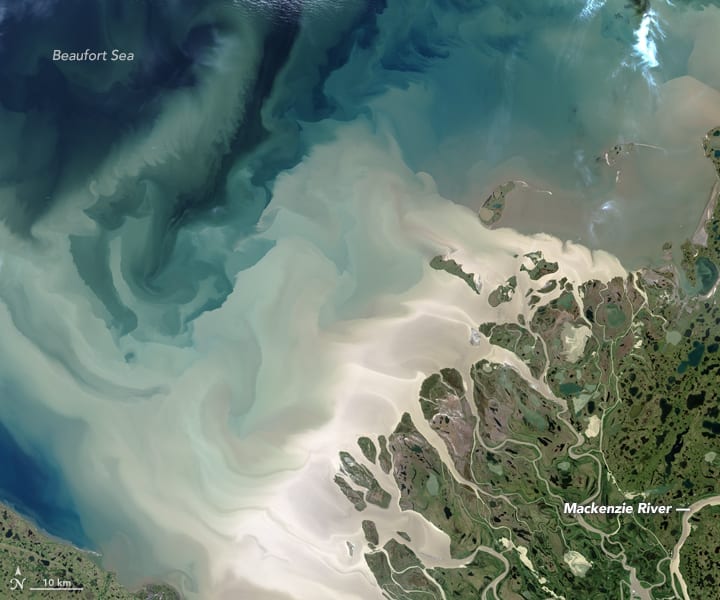
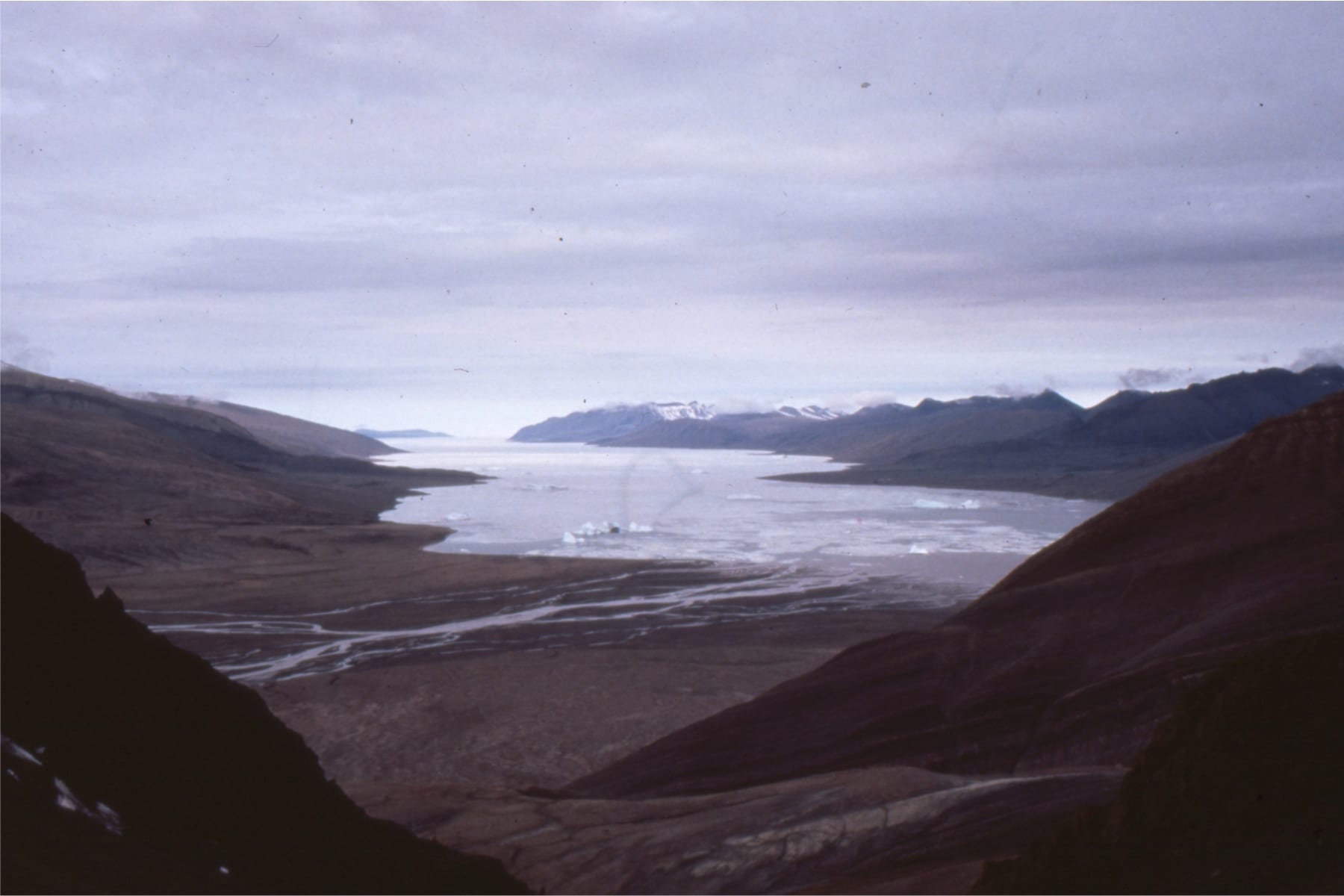
The images are taken from the Late Cretaceous Eureka Sound Group in Sverdrup Basin, Arctic Canada, and the Jurassic-Cretaceous Bowser Basin in northern British Columbia.
Eureka Sound Group


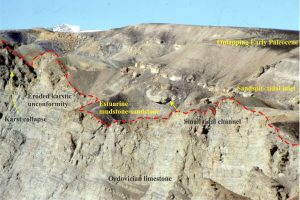

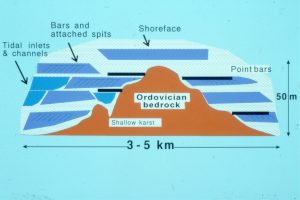










Bowser Basin





Pleistocene-Recent