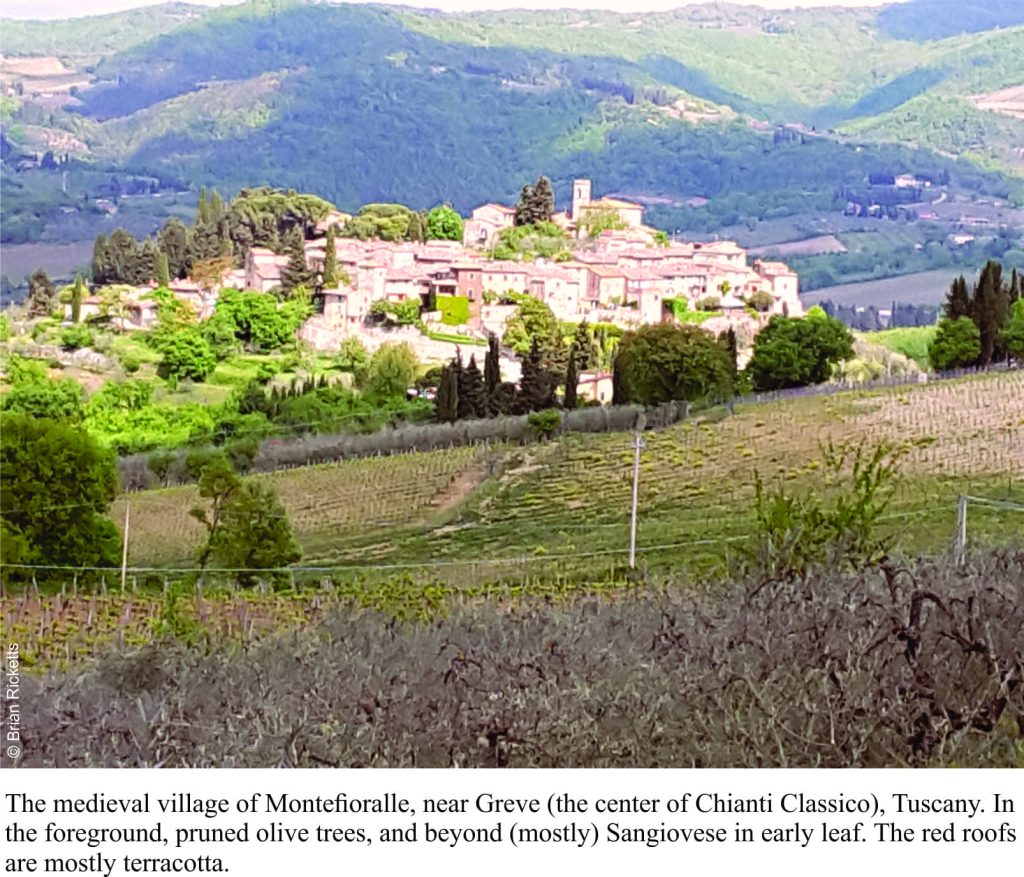
Montefioralle, Chianti country, Tuscany, Italy, and from where I’m sitting (happily sampling a Chianti Classico) I see rolling, wooded hills, next season’s vintage, olive groves, a scattering of farm dwellings, and rock walls. Quintessential Tuscany. Except for a few ratty road cuts, there is little native rock exposed in this part of Tuscany from which a keen geologist might ascertain something of ancient pre-Tuscan history (farther south this changes). But in fact, there are rocks aplenty. Most walls (houses, defensive, retaining, decorative) are made of limestone and sandstone, some quarried and deliberately shaped, as in churches and castello (that date back to the 10th -11th century), and others that made use of whatever was handy at the time. Most of these materials were collected locally; stones that littered the hillsides, and stones brought to the surface during ploughing. Even today, ploughs bring stones to the surface; the local clay-loam soils are incredibly stony (an important part of Chianti terroir).
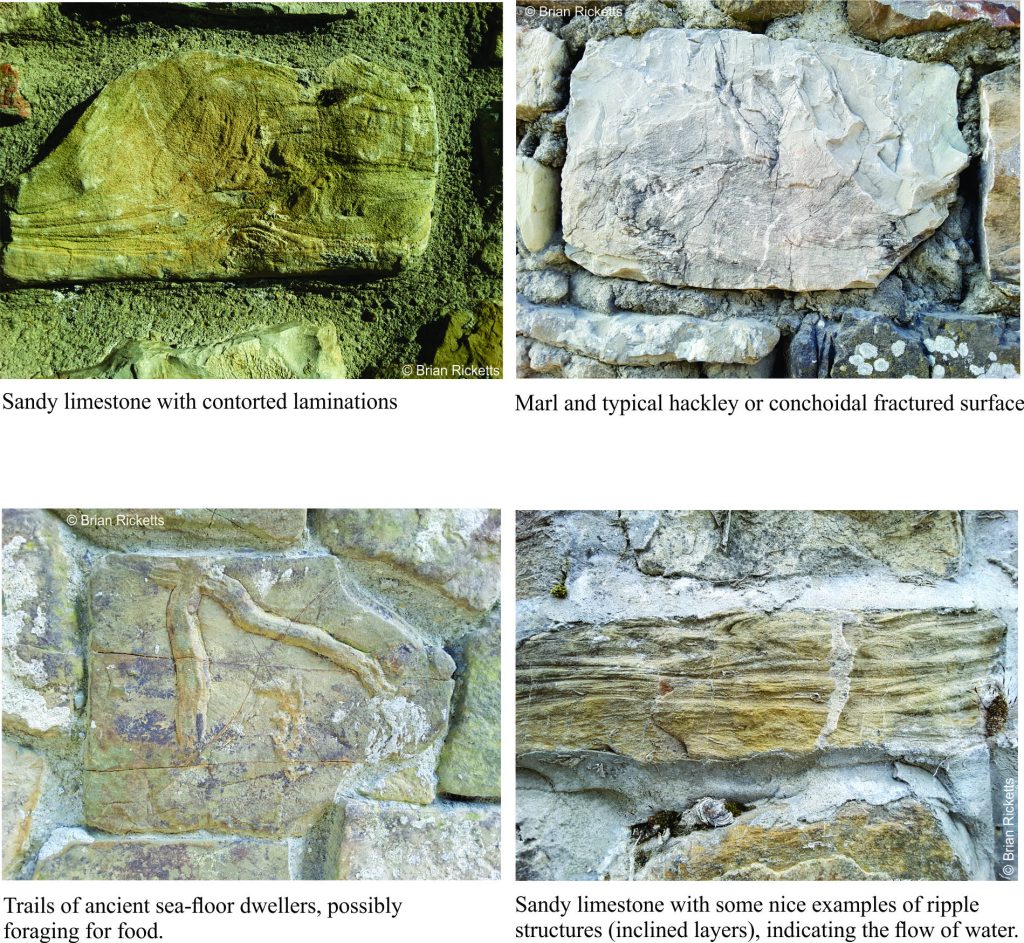
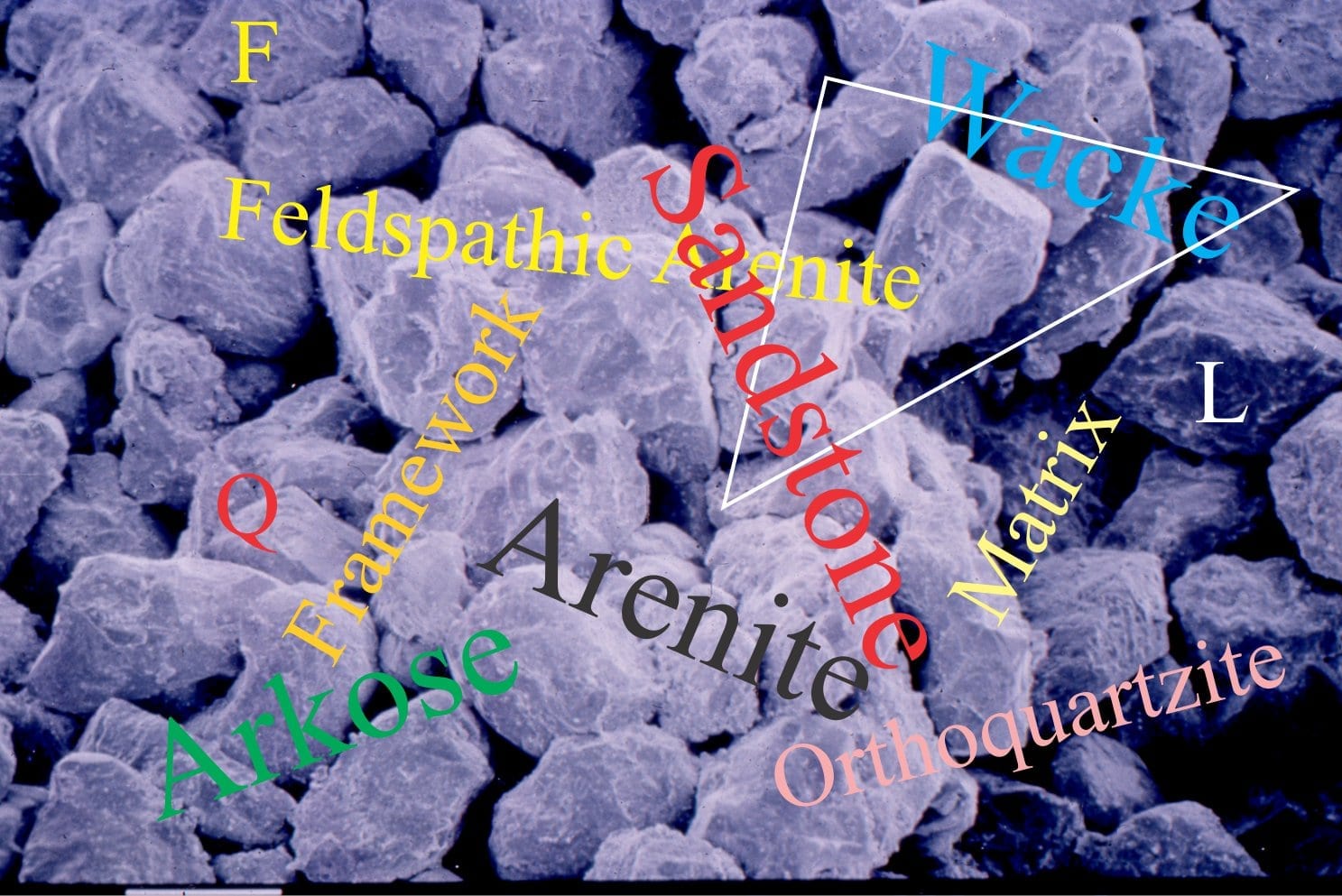
So, despite the paucity of hard-rock exposure, one can make a reasonable guess at the geology beneath the hills and vineyards, based on the stone composition in local buildings. About 50-60% of the stones are cream-coloured marls; marl is an old name (medieval Latin) given to very fine grained, usually muddy limestone that breaks along curved, sharp-edged surfaces (referred to as conchoidal breakage). The Tuscan marls are very hard – ideal for building stone. Variations on this theme include sandy limestones, some of which contain intricate contorted layering, and small crossbeds that indicate flowing water many millions of years ago.
Grey sandstone is also common; in fact it is found as paving stone throughout most of Tuscany. All kinds of structures are visible in these stones, especially cut stones in larger buildings and roads; fossil ripples that indicate flowing water, trails and burrows of critters that moved across or below the ancient seafloor in search of food or finding a place to live. Some of the sandstones are not as hard as the marls, and in places show quite advanced damage where bits of rock fritter away with the vagaries of weather.
An assortment of red bricks, some rumoured to be of Roman or Etruscan derivation, has been used in most walls. It looks like odd-shaped bricks are filling equally odd-shaped gaps, but they have also been used to replace stone arches over doors, or fill holes in walls left by marauding armies (of which there were many), or neglect.
The rocks were originally deposited as sediment in an ancient and vast ocean called Tethys, that separated two supercontinents – Gondwana, and Laurasia (most of Europe and Asia). The Tethys was closed when, about 65 million years ago, the African plate (part of Gondwana) drifted north and crunched into Laurasia. The resulting uplift produced the Apennine Ranges that now course the length of Italy.
Montefioralle is a picturesque hill-top village, typical of many in Tuscany. Its medieval origins are still visible, but frequent battles between neighbouring villages, as well as larger fracas between Florence and Siena, put a few dents in the outer wall and houses. The hill top is crowned by a small church and tower; the last refuge in the event of siege. There is clear evidence of repairs made over the last 800 plus years, including, I suspect, some from a more recent European conflict.
Stones in these Tuscan walls weave their tales in different threads. The limestones and sandstones have a geological story that spans 10s of millions of years, the disappearance of an ocean and the collision of continents. Each stone and brick can also relate centuries of local history; each was carefully placed by someone, a stone-mason or perhaps a Renaissance DIY. Nameless, we can admire their handy-work, wonder what they talked about with their fellow workers, what they ate, who they loved. There are centuries of these former lives everywhere in Tuscany. Chianti Classico loosens all their tongues.











3 thoughts on “The life of a Tuscan wall”
Pingback: medical advice sites
Pingback: work from home jobs
Pingback: sell cartier bracelet fake